Figure 2.
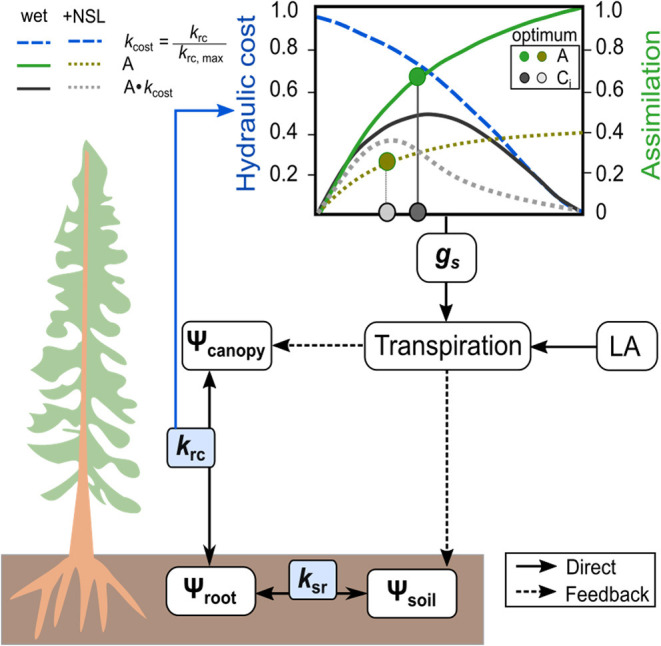
Scheme of the SOX+ model. Soil-to-atmosphere is described as a hydraulic pathway considering three nodes: hydraulic flow from soil to the roots, mediated by soil-to-root conductance (ksr), hydraulic flow from roots to the canopy, mediated by root-to-canopy conductance (krc), and hydraulic flow from the canopy to the atmosphere, mediated by stomatal conductance (gs). The optimum gs is determined by considering the photosynthetic gain (A) multiplied by the hydraulic cost function (kcost), which describes the decreases in krc as Ψcanopy becomes more negative. Transpiration is calculated at the tree level by multiplying gs and leaf area, and it has a direct effect on canopy water potential, an indirect effect on soil water content, and therefore on Ψsoil. Non-stomatal limitations of photosynthesis (NSL) decrease optimum stomatal conductance because of limiting A when Ψcanopy declines below a predefined threshold.
