Fig. 2. Pancreatic Cancer Pathogenesis.
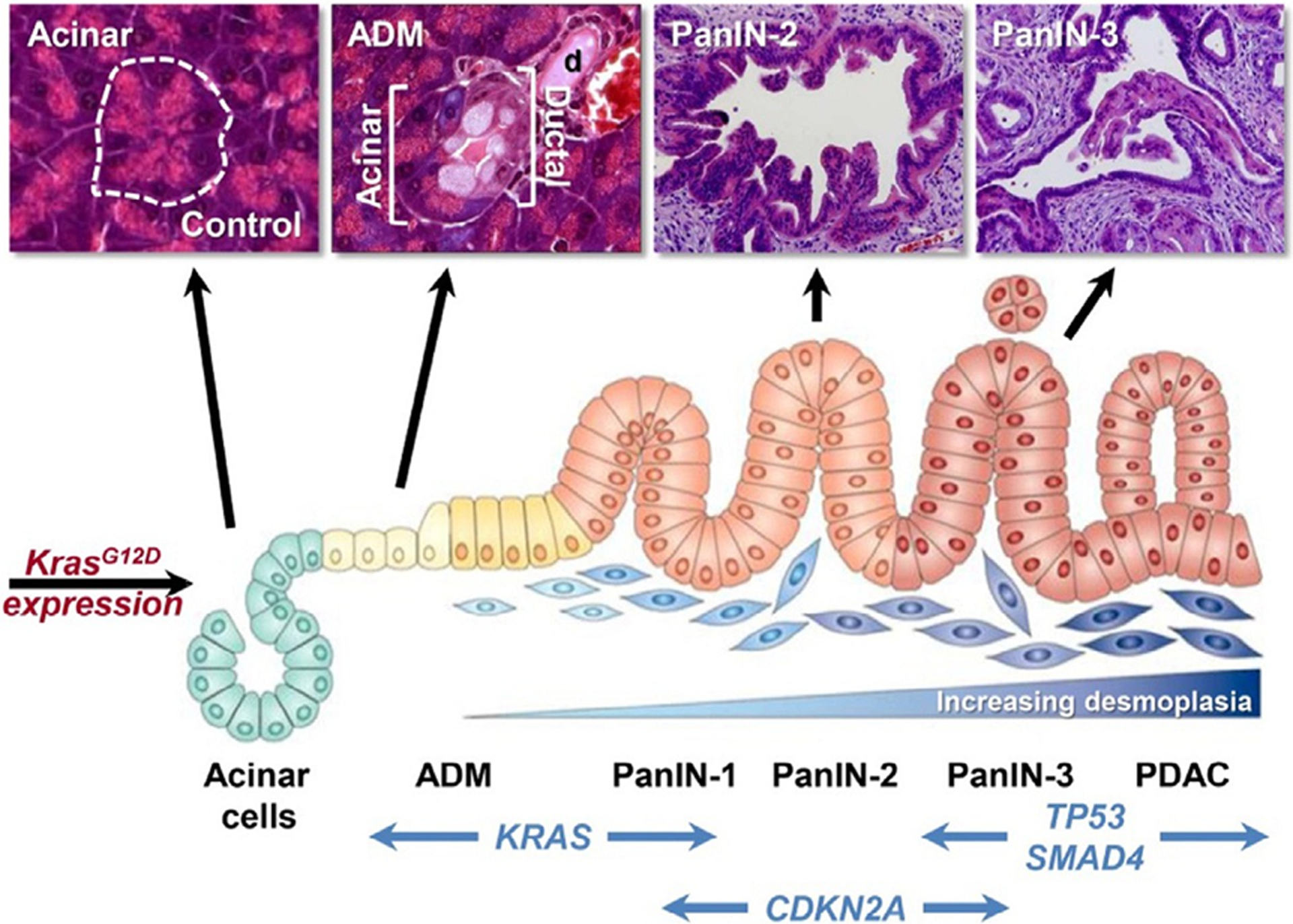
The schematic and mouse histology demonstrate step-wise development of pancreatic cancer. The accumulation of driver mutations such as KRAS, CDKN21, TP53, and SMAD4 induces the transformation of normal acinar cells to acinar-to-ductal metaplasia (ADM), pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN), and eventually pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Adapted from reference [1] with permission from Elsevier.
