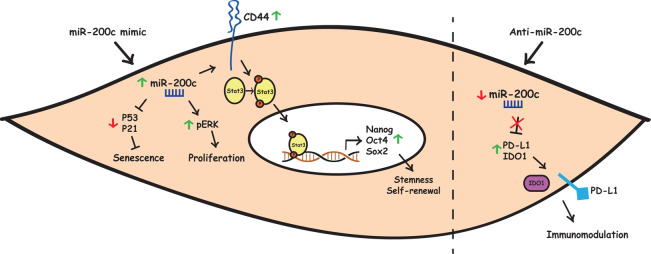
Fig 6. Graphical summary of how miR-200c-3p may regulate self-renewal, proliferation, senescence and have immunomodulatory effect in ASCs.
Left: in the cytoplasm, over-expression of miR-200c-3p (green arrow) may stimulate cell proliferation through an increase of p-ERK and inhibit cell senescence by downregulating p53/p21 axis (red arrow). MiR-200c-3p can also increase CD44 expression leading to STAT3 phosphorylation, which in turn may activate transcription of stemness-related genes in the nucleus. Right: Inhibition of miR-200c-3p with a specific anti-miR (red arrow) alleviates repression of PD-L1 and IDO-1, the inhibitory checkpoints, to regulate immune responses against ASCs.