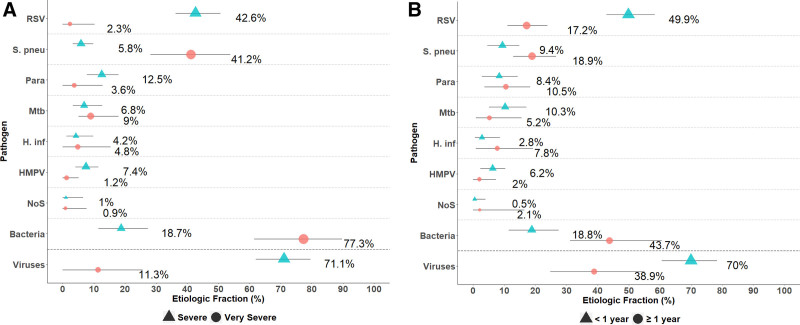
FIGURE 4.
Integrated etiology results, CXR+ cases, by (A) pneumonia severity and (B) age, selected pathogens. CXR+ defined as consolidation and/or other infiltrate on chest radiograph. Bacterial summary excludes Mtb. Very severe pneumonia defined as cough or difficulty breathing, and at least one of the following: central cyanosis, difficulty breast-feeding/drinking, vomiting everything, convulsions, lethargy, unconsciousness or head nodding. Sample sizes: CXR+ severe, N = 247; CXR+ very severe, N = 39. CXR+ <1 year, N = 177; CXR+ ≥1 year, N = 109. Pathogens that were estimated at the subspecies level but grouped to the species level for display include Parainfluenza virus types 1, 2, 3 and 4; S. pneumoniae PCV 10 and S. pneumoniae non-PCV 10 types; and H. influenzae type b and H. influenzae non-type b. Line represents the 95% credible interval. The size of the symbol is scaled based on the ratio of the estimated etiologic fraction to its standard error. Of two identical etiologic fraction estimates, the estimate associated with a larger symbol is more informed by the data than the priors. H. inf indicates Haemophilus influenzae; HMPV, human metapneumovirus A/B; Mtb, Mycobacterium tuberculosis; NoS, not otherwise specified (ie, pathogens not tested for); Parainfluenza virus types 1, 2, 3 and 4; Respiratory syncytial virus A/B; S. pneu, Streptococcus pneumoniae.