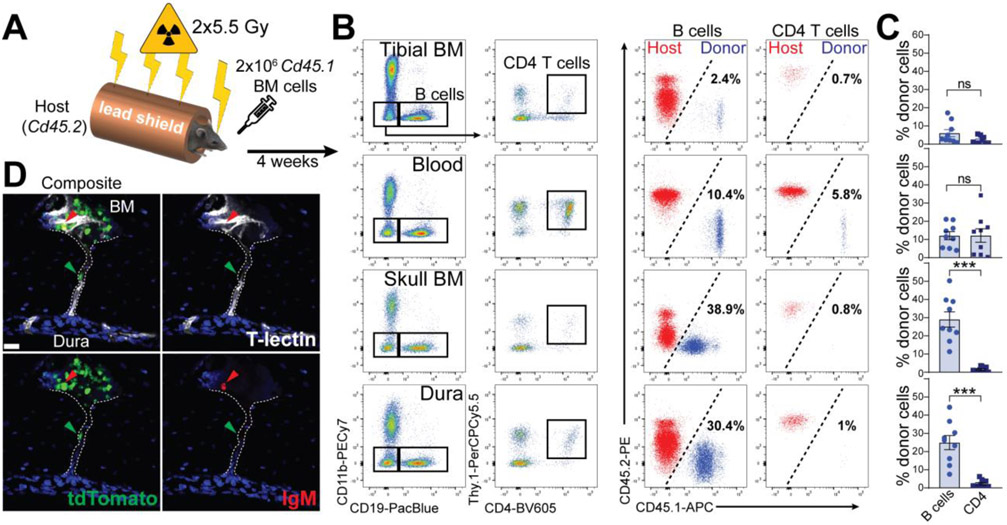
Fig. 5. Skull BM chimeras demonstrate that dura B cells originate from the calvaria.
(A) Schematic depiction of the experimental design of calvaria BM transplantation. (B) Representative flow cytometry plots of B cells (gated on CD19+CD11b− cells) and CD4 T cells (gated on CD19−CD11b−Thy.1+CD4+ cells) from multiple compartments in recipient mice (left). Percentage of donor-derived (CD45.1+) and host-derived (CD45.2+) B and CD4 T cells are shown (right). (C) Frequency of donor-derived B cells and CD4 T cells per compartment (mean ± SEM; n=9 mice; Mann Whitney U test ***P<0.001; data generated from two independent experiments). (D) Representative confocal image of an IgM− B cell trafficking from the calvarial BM towards meninges through a skull vascular channel.