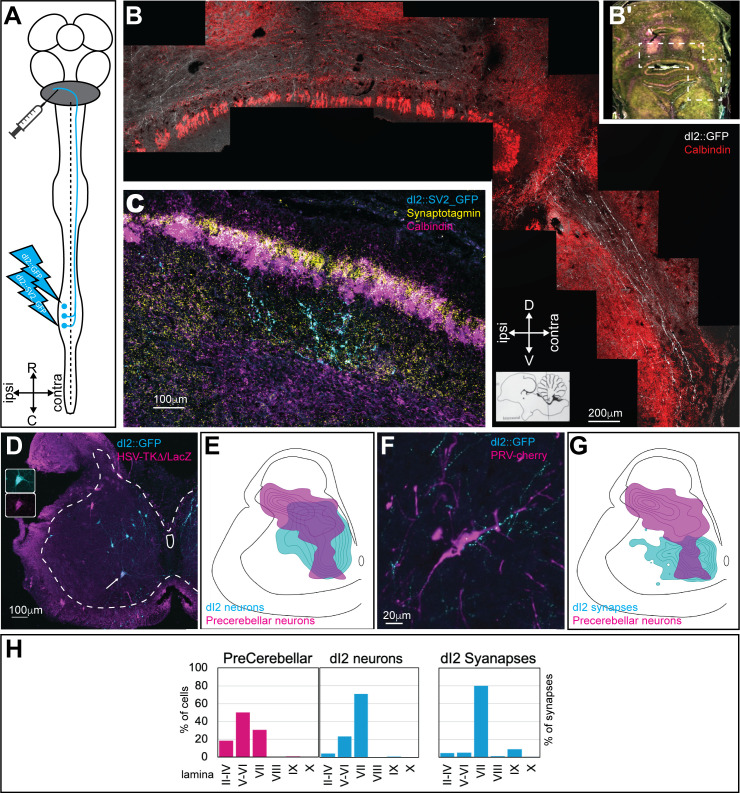
Figure 2. dI2 neurons project to the cerebellum.
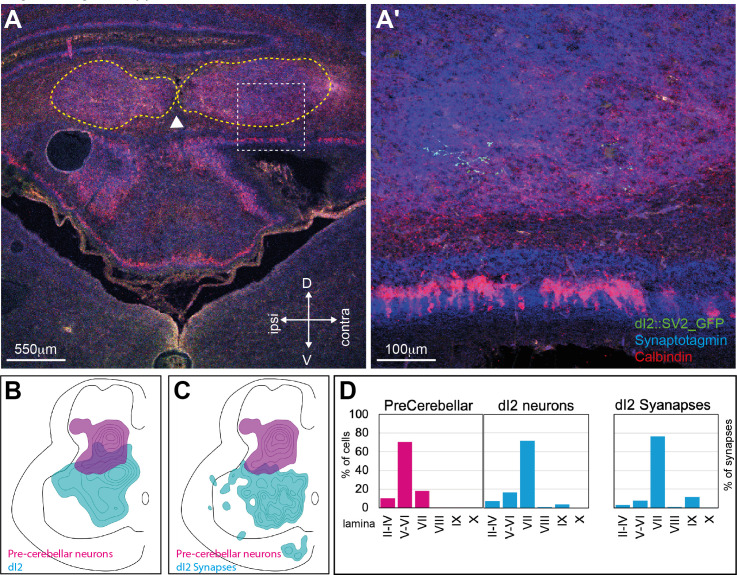
(A) Experimental setup for labeling dI2 neurons that project to the cerebellum. dI2 neurons were genetically targeted at HH18, and precerebellar neurons were labeled using intracerebellar injection of replication-defective HSV-LacZ or PRV-Cherry at embryonic day (E) 15. The abbreviations in the coordinates: R: rostral; C: caudal. (B) A cross-section of E17 brainstem and cerebellum. The dashed polygon in (B′) is magnified in (B). dI2 axons reach the cerebellum, enter into it via the superior cerebellar peduncle, and cross the cerebellar midline. Calbindin (Purkinje neurons, magenta [B′] or red [B]). Abbreviations in the coordinates: D: dorsal; V: ventral. (C) A cross-section of E17 cerebellar cortex. Lumbar-originating dI2 synapses (cyan) in the granular layer of the anterior cerebellar cortex. Calbindin (Purkinje neurons, magenta), synaptotagmin (yellow). (D) A cross-section of an E15 embryo at the lumbar spinal cord level (sciatic plexus level). Precerebellar neurons were infected and labeled with HSV-LacZ (magenta), and dI2 neurons expressed GFP (cyan). A large-diameter dI2 neuron coexpressing LacZ and GFP is indicated by an arrow (magnification of the two channels in the insets). (E) Density plots of dI2 and precerebellar neurons (density values 10–90%) in the sciatic plexus segments (N = 374 and N = 289 cells, respectively). (F) PRV-Cherry-labeled precerebellar neurons (magenta) are in contact with dI2 axonal terminals (cyan). (G) Density plots of dI2 synapses and precerebellar neuron somata (density values 10–90%) in the sciatic plexus segments (N = 4735 synapses and N = 289 cells, respectively). (H) The laminar distribution of precerebellar neurons, dI2 neurons, and dI2 synapses at the sciatic level. See Figure 2—source data 1.