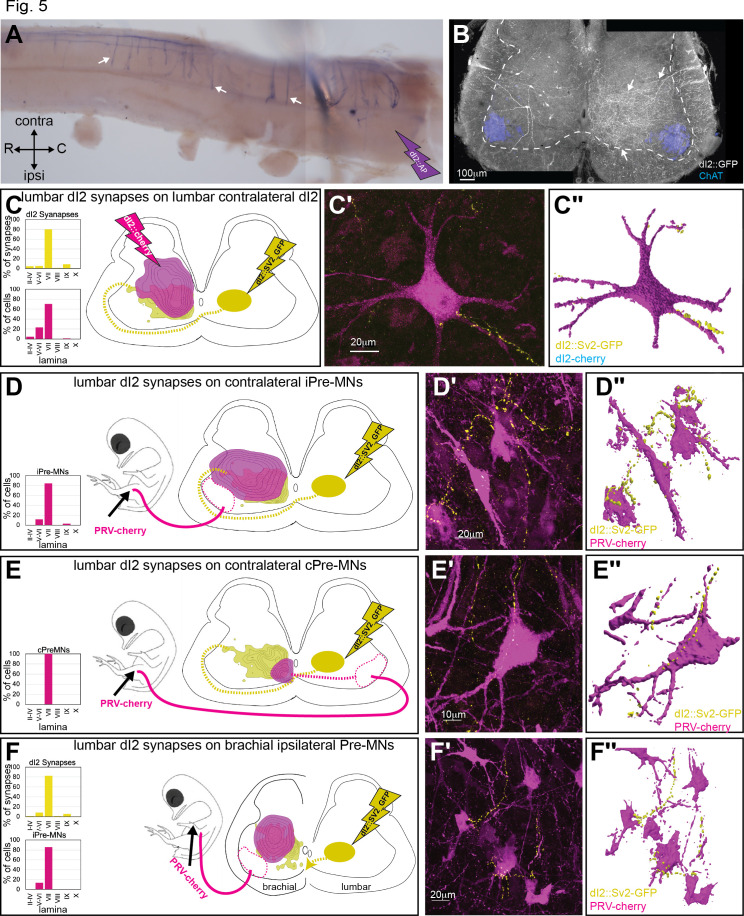
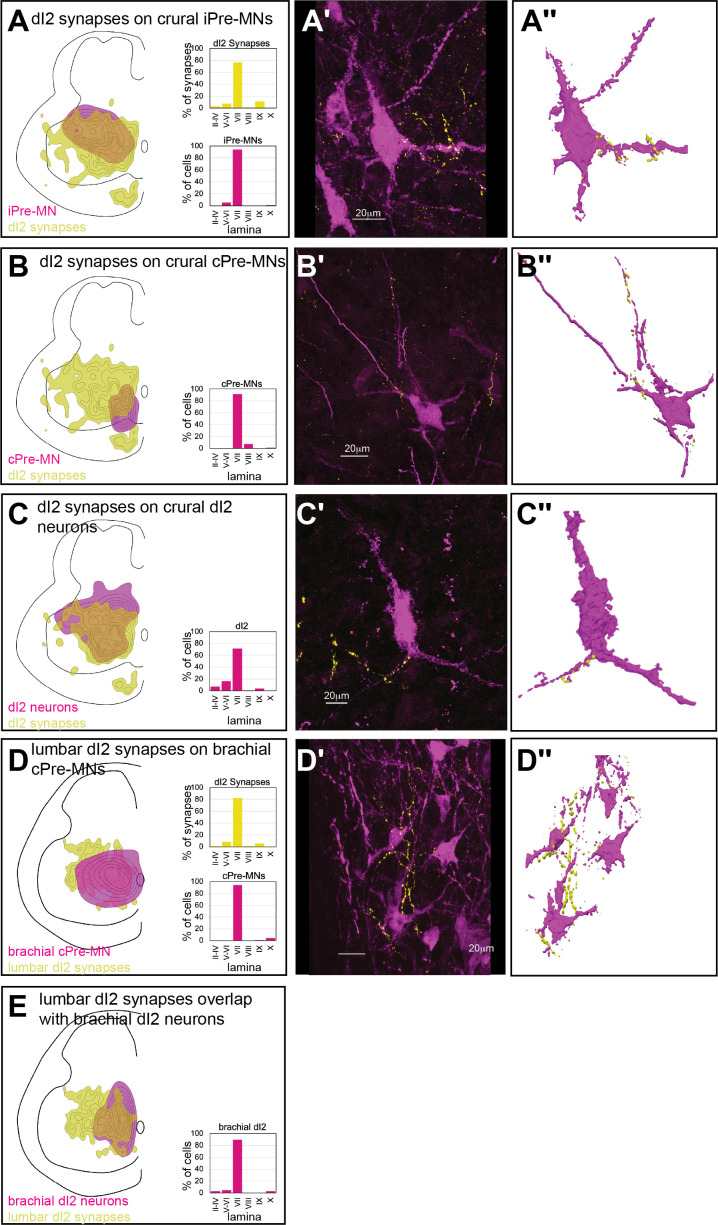
Figure 5. Spinal synaptic targets of dI2 neurons.
(A) Whole-mount staining of the spinal cord (thoracic segments) expressing alkaline phosphatase (AP) in dI2 neurons. The lumbar dI2 neurons (not included in the image) were labeled with AP. dI2 axon collaterals project and into the spinal cord (arrows). Abbreviations in the coordinates: rostral: R: caudal: C. (B) Cross-section of an embryonic day (E) 17 embryo at the crural plexus level of the lumbar spinal cord. Axonal collaterals (white arrow) penetrating the gray matter of the contralateral side are evident. Schematic representations of the experimental design for labeling synapses (dI2::SV2-GFP, yellow) and potential targets (magenta) supplemented by cell soma density and dI2 synaptic densities are illustrated in (C–F). The laminar distribution of the somata and synapses is illustrated on the right side of (C–F). Examples of target neurons contacting synaptic boutons of dl2 neurons are shown in (C′–F′), and their 3D reconstruction is shown in (C″–F″). Genetic labeling was achieved using dI2 enhancers (Figure 1—figure supplement 1A) electroporated at HH18. Premotor neurons (pre-MNs) were labeled by injection of PRV-Cherry into the hindlimbs (D, E) or the forelimb (F) musculature at E13. The embryos were incubated until the pre-MNs were infected (39 hr). (C) dI2 neurons innervate contralateral dI2 neurons (N = 4735 synapses and N = 374 cells, respectively, two embryos). (D) dI2 neurons innervate ipsilateral projections of pre-MNs at the sciatic plexus level (N = 4735 synapses and N = 936 cells, respectively, scheme was done based on one representative embryo). (E) dI2 neurons innervate contralaterally projecting pre-MNs at the sciatic plexus level (N = 4735 synapses and N = 47 cells, respectively, scheme was done based on one representative embryo). (F) dI2 neurons innervate ipsilaterally projecting pre-MNs at the brachial level (N = 2215 synapses and N = 286 cells, respectively, three embryos). See Figure 5—source data 1.