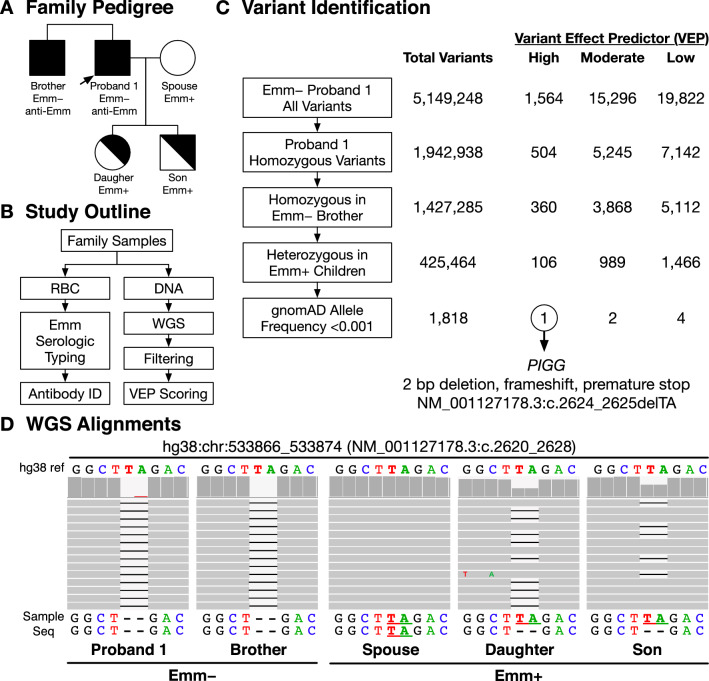
Figure 1.
(A) Family Pedigree. Emm RBC phenotypes shown include the Proband and his brother (both with anti-Emm in the plasma). Also shown are the Proband's spouse and two children who are Emm+ and were shown to lack the antibody. (B) Study Outline. Emm serologic RBC typing was performed with in-house reagents and short read whole genome sequencing (WGS). (C) Variant Identification. Illustration of the strategy used to enrich for loss of function mutations associated with familial inheritance and variant effector prediction (VEP) scoring to identify the genetic cause of the Emm− phenotype. PIGG was the only candidate gene that passed our filtering strategy. (D) WGS alignments. IGV genomics viewer shows the wild type sequence (upper) and PIGG Exon 12 biallelic sequence for each family member (below). Individual sequence reads are shown in gray for positions corresponding to the hg38 reference sequence with bar plots above (dark grey) reflecting the relative number of reads at that position. Emm− family members were homozygous for a 2-bp deletion in Exon 12, predicted to cause a frameshift and premature stop, designated in as c.2624_2625delTA, p.(Leu875*), rs771819481, and chromosomal location hg38:chr4:533870_533871delTA. The spouse was wild type, and the daughter and son are heterozygous.