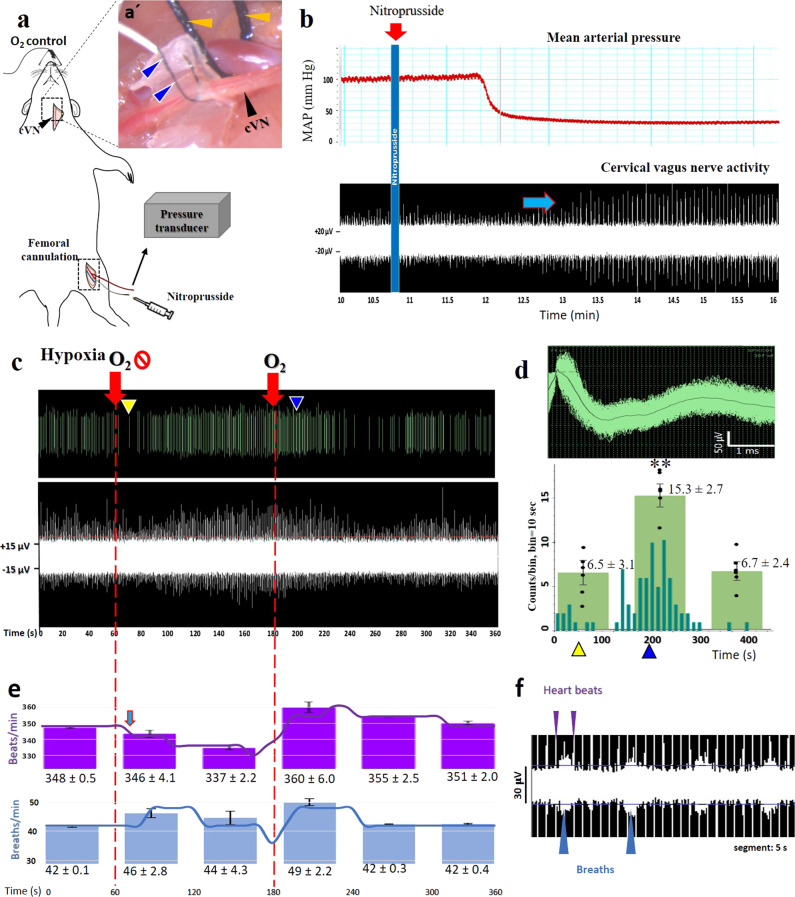
Fig. 2. Vagal neuronal activity evoked by hypotension and hypoxia recorded by sutrode.
a Schematic of sutrode placement on the rat cVN, with a femoral arterial blood pressure sensor. a’ The cVN (black arrow) was interfaced with a sutrode (blue arrows). A conventional 4-0 nylon suture was used to isolate the carotid artery (yellow arrows). b Nitroprusside (red arrow) induced hypotension, that correlated with an increase in cVN firing rate (blue arrow). c Oxygen restriction induced an initial decrease (yellow arrowheads) and a subsequent 10-fold increase (blue arrowheads) in vagal activity. d Representative rate histogram of an isolated waveform (dark green bars), and graph (overlapped) of average total neuronal activity n = 6 experiments from n = 3 rats (averages ± SD), whiskers represent confidence intervals **p < 0.01. Oxygen restriction and restoration are pointed as red arrows in c. e The Oxygen reduction corresponded to a slight decrease in heart rate (blue arrow), and a subsequent increase in respiration rate calculated from f unfiltered raw data files. Values are from a representative rat, and overlapped bars are presented as the average ± SD of three rats.