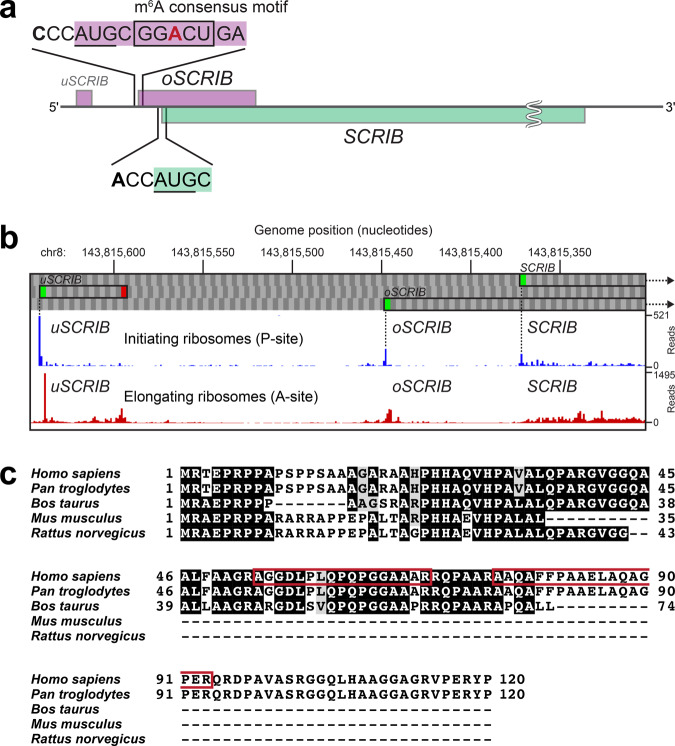
Fig. 2. Investigation of the newly discovered oSCRIB protein.
a The transcript encoding the main SCRIB protein contains additional unidentified sORFs (uSCRIB and oSCRIB). The oSCRIB-coding region overlapped the downstream out-of-frame SCRIB gene in the human genome. Translational start codons (AUGs) of oSCRIB and SCRIB and the surrounding sequences in humans are shown. The most prevalent sequence (GGACU) for the reversible epitranscriptomic m6A modification and the resultant m6A-dependent start codon selection42,43,58,73 are shown in the box. b Survey of publicly available Ribo-Seq data. The aggregated profiles of initiating and elongating ribosomes were obtained from GWIPS-viz74 (https://gwips.ucc.ie). c Translation products of oSCRIB in humans (Homo sapiens), chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes), cattle (Bos taurus), mice (Mus musculus), and rats (Rattus norvegicus). The protein sequences were aligned and colored using the GenomeNet ClustalW 2.1 and EMBnet BoxShade 3.21 servers (https://www.genome.jp/tools-bin/clustalw and https://embnet.vital-it.ch/software/BOX_form.html). Red boxes indicate the amino acid sequences of tryptic peptides detected in LC–MS/MS analyses as shown in Figs. 3 and 4.