Figure 7. Inhibiting C3aR activity ameliorates O-exo–mediated detrimental effects in the aged ischemic brain.
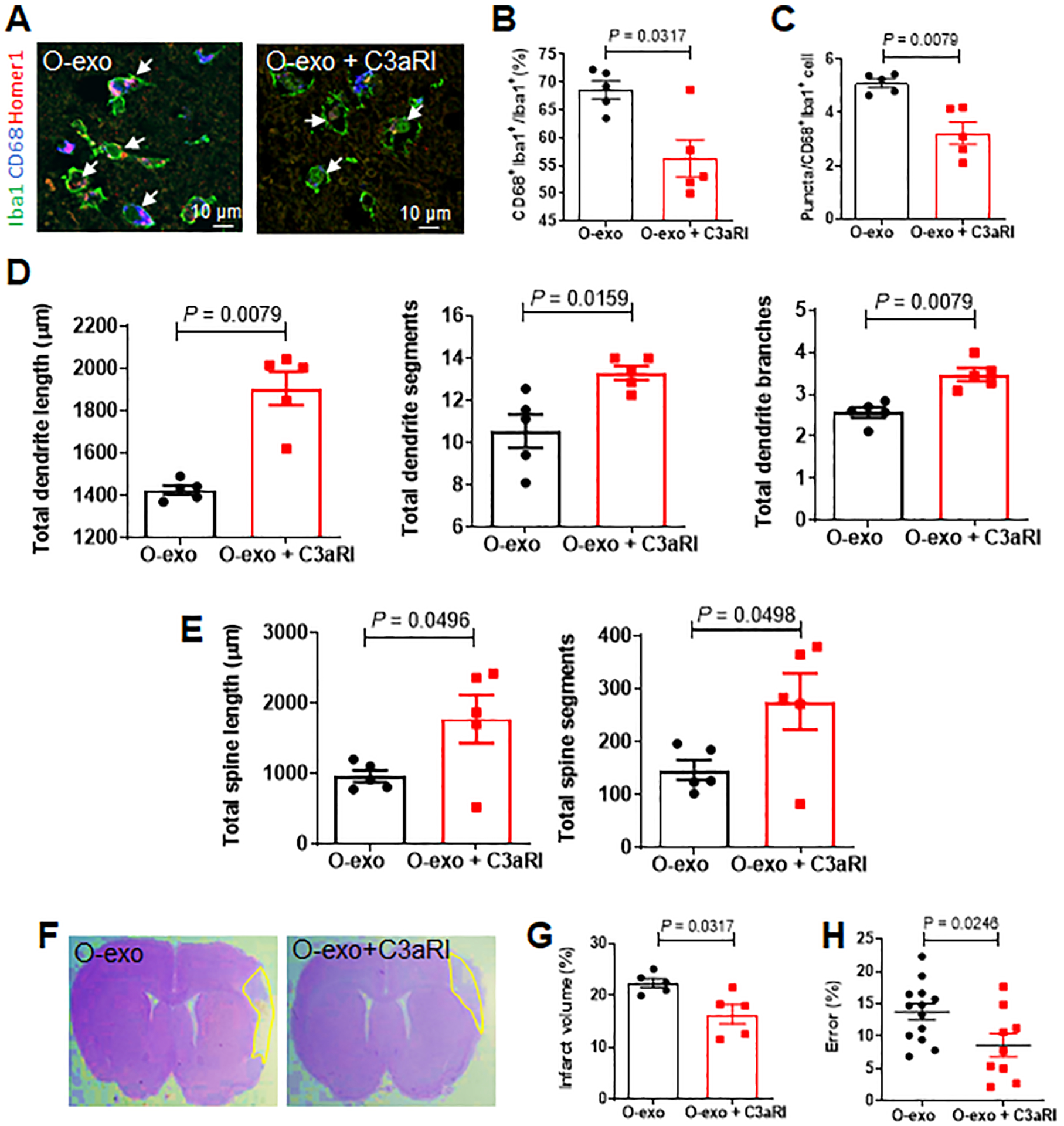
A. Confocal images showing Iba1 (green), CD68 (blue) and Homer1 (red) expression in the penumbra in aged ischemic rats treated with O-exo or a combination of O-exo and C3aR inhibitor (C3aRI). White arrows indicate Iba1+CD68+Homer1+ microglia. B. Quantification of Iba1+CD68+ activated microglia in aged ischemic rats 72 h after injection of O-exo with or without C3aRI (N = 5 per group). The P values were assessed by a Mann-Whitney test. C. Quantification of triple+ puncta per Iba1+ cells in the aged ischemic brain after injection of O-exo with and without C3aRI (N = 5 per group). The P values were assessed by a Mann-Whitney test. D, E. Quantification of total dendritic length (D), segments and branches and total spine length and segments (E) in the penumbra of aged ischemic rats 72 h after O-exo injection with or without C3aRI (N = 5 per group). The P values were assessed by a Mann-Whitney test. F. Representative CV-stained images showing infarct area in animals treated with O-exo alone or combination of O-exo and C3aRI. G. Infarct volume in aged ischemic rats treated with O-exo alone or combination of O-exo and C3aRI (N = 5 per group). The P values were assessed by a Mann-Whitney test. H. Sensorimotor deficits were determined by the ladder rung walking test in aged ischemic rats treated with O-exo alone or combination of O-exo and C3aRI. Data represent mean ± SEM. Each data point represents a biological replicate. The P values were assessed by unpaired Student’s t-test. O-exo, serum exosomes from aged rats.
