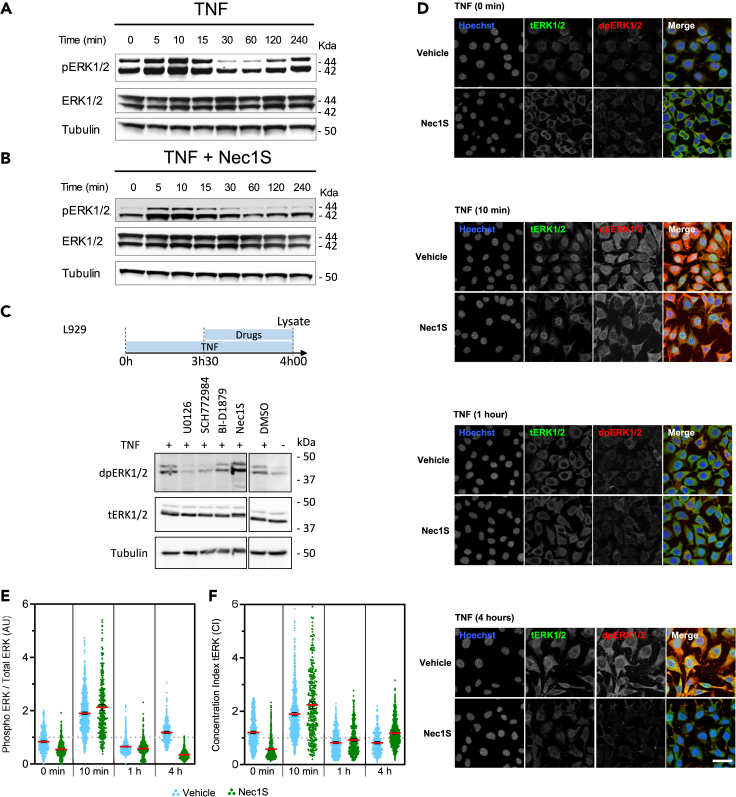
Figure 2.
Spatio-temporal patterns of activated ERK1/2 during TNF-induced necroptosis in L929
(A and B) L929 cells were serum-deprived (1% FCS) for 12 h and then pretreated (B) or not (A) for 30 min with Nec1S (10 μM) and subsequently stimulated with TNF for the indicated time points. Cells were then lysed and immunoblotted as indicated on the left of each blot.
(C) L929 cells were serum-deprived (1% FCS) for 12h and then treated, harvested, and lysed according to the temporal scheme (C, upper) for immunoblotting. Corresponding molecular weights are indicated on the right of each blot.
(D) L929 cells were serum-deprived (FCS 1%) for 12h and then pretreated or not with Nec1S (10 μM) for 30 min and subsequently stimulated with TNF. Cells were then fixed and processed for immunofluorescence, at the indicated time points, with an antibody against total ERK1/2 (tERK1/2, green) and di-phosphorylated activated ERK1/2 (dpERK1/2, red) and stained for DNA with Hoechst (blue). DMSO (vehicle) was added as control at a volume equivalent to 10 μM Nec1S treatment condition. Scale bar: 50 μm.
(E and F) Scatter plots showing levels of phosphorylated ERK1/2 (E) and subcellular distribution (concentration index of ERK1/2 distribution between the nucleus and the cytoplasm) of total ERK1/2 (F) at the indicated time points in cells undergoing necroptosis (DMSO, blue) or in which necroptosis was inhibited by Nec1S (green). Data are presented as mean ±95 CI of at least two independent experiments, with at least 300 single cells analyzed per condition. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. Significance between samples is indicated as follows: ∗p< 0.05; ∗∗p< 0.01; ∗∗∗p< 0.001; NS, not significant. Note that all differences were significant but not indicated.