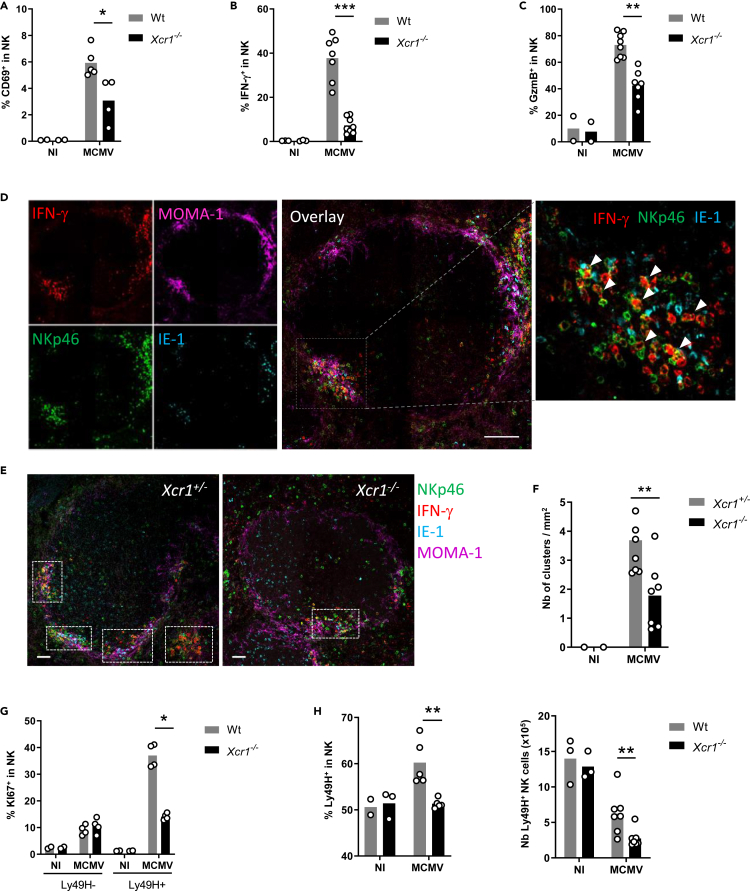
Figure 1.
XCR1 promotes NK cell activation and redistribution in the spleen upon MCMV infection
(A–C) Spleens of Xcr1−/− mice and Wt controls were harvested 40 h (A–F), 4 days (G), and 5 days (H) after MCMV infection. Splenic NK cells (NK1.1+TCRβ−) were stained for CD69 (A) and intracellularly for IFN-γ (B) and GzmB (C) directly ex vivo.
(D) Visualization of activated NK cell clusters in the spleens of MCMV-infected mice. Scale bar: 50 μm.
(E) Analysis of NK cell clusters in Xcr1−/− vs littermate controls upon MCMV infection. Spleen sections were prepared from KarmaCre;Rosa26tdRFP;Xcr1−/− mice and KarmaCre;Rosa26tdRFP;Xcr1+/− controls and stained for NKp46 (green), MOMA-1 (purple), IFN-γ (red), and IE-1 (cyan). Inserts show examples of clusters areas as defined in the material and methods. NK cell clusters were identified as groups of at least 10 IFN-γ+ cells, encompassing NKp46+ cells and gathered around MCMV-infected cells (IE-1+) in the marginal zone (MOMA-1+). Scale bar: 50 μm.
(F) Quantification of NK cell clusters in the spleens of MCMV-infected KarmaCre;Rosa26tdRFP;Xcr1−/− mice and their littermate Xcr1+/− control 40 h after infection.
(G) Splenic NK cells (NK1.1+TCRβ−) were stained intracellularly for KI67 4 days after infection.
(H) Proportion and absolute number of Ly49H+ NK cells in Wt vs Xcr1−/− mice 5 days after infection. One experiment representative of at least 4 independent ones with at least 4 mice per infected group is shown, except for B-E, where two experiments with at least 3 mice per group were pooled. NI, noninfected; ∗, p < 0.05; ∗∗, p < 0.01; ∗∗∗, p < 0.001.
See also Figure S1.