Figure 5.
NK cell delivery of GM-CSF to cDC1 requires physical contacts to trigger CCR7 upregulation on cDC1
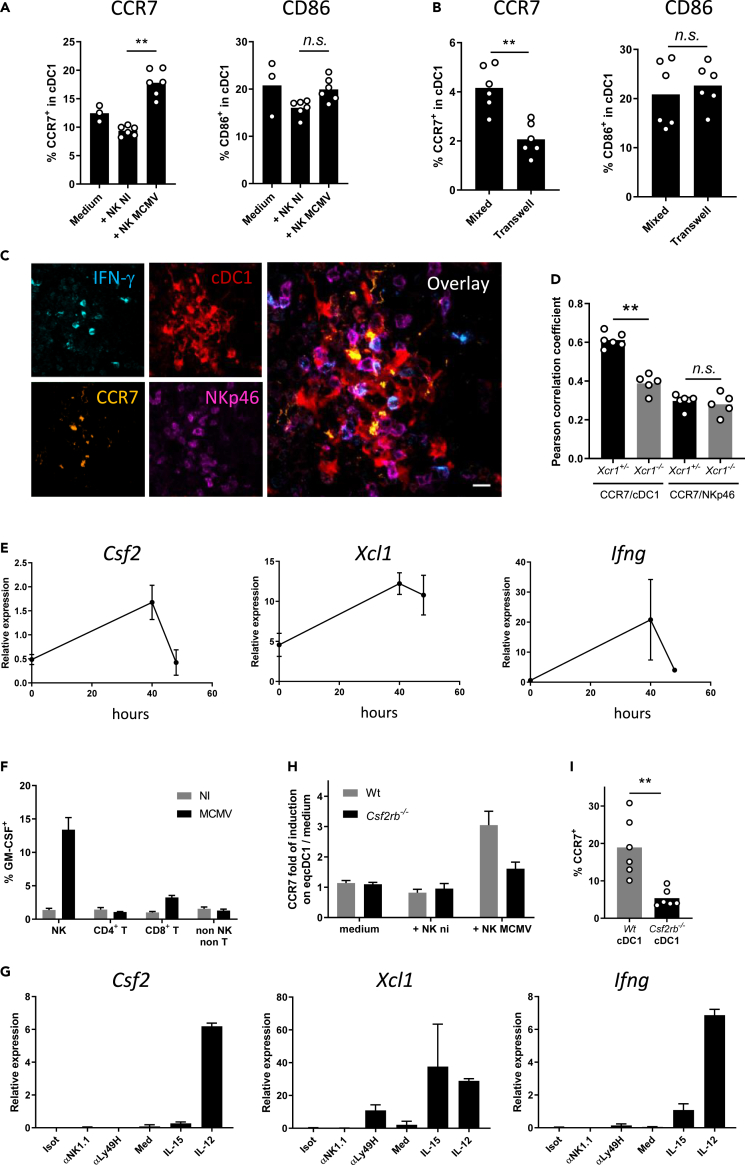
(A and B) Analysis of CCR7 and CD86 expression on cDC1 when in coculture for 7 h with NK cells from spleens of Wt mice infected or not for 40 h with MCMV. cDC1 and NK cells were cocultured either in the same well (A) or separated by a 0.4-um-diameter pore-bearing transwell apparatus (B). One representative experiment of two independent ones with at least four mice per group is shown. n.s., nonsignificant; ∗, p < 0.05.
(C) Analysis of CCR7 expression on cDC1 in NK cell clusters 40 h after MCMV infection. Spleen sections of KarmaCre;Rosa26tdRFP mice were stained for IFN-γ, NKp46, CCR7, and tdRFP (cDC1). This cluster was imaged in the marginal area. The micrograph shown is representative of the analyses of 4 mice, from two independent experiments. Scale bar: 10 μm.
(D) Coefficients of Pearson correlation between CCR7 staining and tdRFP expression as detected in clusters (C) of KarmaCre;Rosa26tdRFP;Xcr1−/− mice and their Xcr1+/− littermate controls. Coefficients of Pearson correlation between CCR7 and NKp46 stainings are shown as controls. Two independent experiments with at least 2-3 mice per group were pooled. ∗∗, p < 0.01; n.s., nonsignificant.
(E) Kinetics of induction of Csf2 (Gmcsf) expression in total spleen during MCMV infection. Total RNA was extracted from spleens from Wt mice at the indicated times after MCMV infection, and RT-qPCR was performed using Hprt as a housekeeping gene. Data are represented as mean (+/− SD). One representative experiment of two independent ones with at least 4 mice per group is shown.
(F) Analysis of GM-CSF production by different lymphocyte populations 40 h after MCMV infection. Splenocytes were intracellularly stained for GM-CSF. Data are represented as mean (+/− SEM).
(G) RT-qPCR analysis of Csf2, Xcl1 and Ifng expression in purified NK cells activated in vitro with different stimuli. Data are represented as mean (+/− SEM). Isot, Isotype; med, medium.
(H) Analysis of CCR7 upregulation on Csf2rb-deficient eqcDC1 by activated NK cells. Wt and Csf2rb-deficient immature eqcDC1 were enriched from FLT3-L BM cultures and cocultured for 7 h with NK cells purified from spleens of mice infected or not for 40 h with MCMV. eqcDC1 were gated as CD11c+SiglecH−SIRPα−CD24+ cells. Data are represented as mean (+/− SEM).
(I) Analysis of CCR7 expression on Wt vs Csf2rb−/− cDC1 from Wt:Csf2rb−/− mouse chimeras 48 h after infection. ∗∗, p < 0.01. Error bars represent standard deviations.
See also Figure S5.