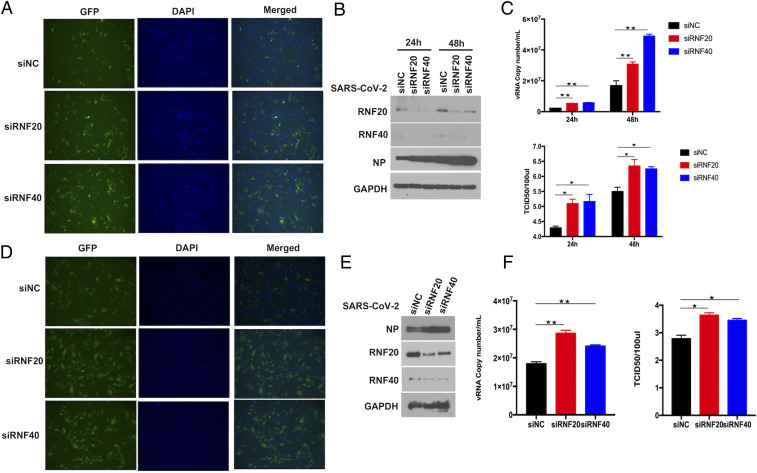
Fig. 3.
RNF20/RNF40 complex inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication. (A) Microscopy images of Huh7 cells transfected with Scramble siRNA (siNC) and siRNA against RNF20 or RNF40. At 48 h posttransfection, cells were challenged with SARS-CoV-2 GFP reporter virus (0.01 MOI) for 24 h to monitor SARS-CoV-2 replication. (B) The siRNA targeting RNF20 or RNF40 was transfected in Huh7 cells, which were infected at 48 h posttransfection with SARS-CoV-2 GFP reporter virus at an MOI of 0.01 and incubated for additional 24 h or 48 h. SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein expression level was determined by Western blot. (C) The levels of SARS-CoV-2 genome copy in the supernatant were determined by real-time PCR assay. The supernatants were also harvested for viral titer measurement by TCID50 assay performed in Vero-E6 cells. (D) ACE2-HeLa cells were transfected with siRNA against the indicated genes for 48 h and then infected with SARS-CoV-2 GFP reporter virus at an MOI of 0.01 and incubated for 24 h. The GFP protein was observed by fluorescence microscopy. (E) The indicated siRNAs were transfected in ACE2-HeLa cells, which were infected 48 h later with SARS-CoV-2 GFP reporter virus at an MOI of 0.01 and incubated for an additional 24 h. SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein expression level was determined by Western blot. (F) The virus titers were evaluated by TCID50 assay. Virus RNA copy numbers in the supernatant were measured by real-time PCR. Magnification is 10X for all fluorescene microscopy images. Results are expressed as the mean ± SD (error bar) of three independent experiments; asterisks in C and F represent statistical significance based on two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).