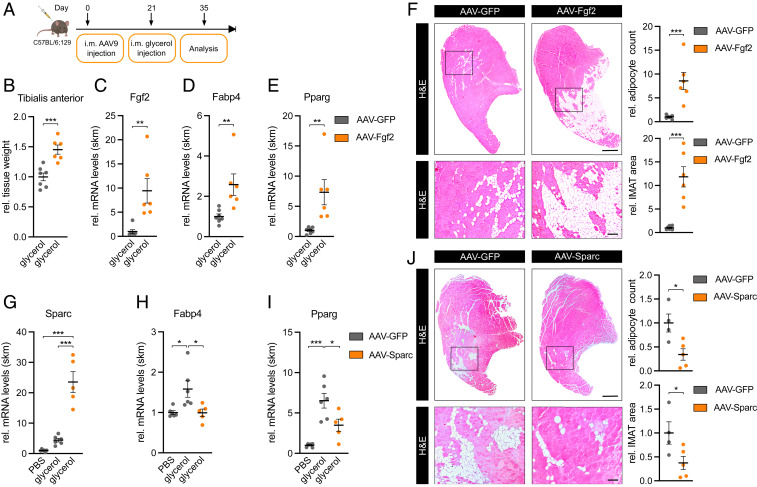
Fig. 6.
FGF-2 and SPARC are regulators of IMAT formation. (A) Experimental overview of intramuscular (i.m.) AAV9 injections. (B) Relative tissue weight and (C) Fgf2, (D) Fabp4, and (E) Pparg expression in AAV-Fgf2–infected tibialis anterior muscle 2 wk after glycerol injection (n = 7 versus 6). qPCR values were normalized to 18S ribosomal RNA (rRNA). (F and J) IMAT formation in representative hematoxylin and eosin staining of transverse sections in (F) AAV-Fgf2– (n = 7 versus 6) or (J) AAV-Sparc– (n = 4 versus 5) infected tibialis anterior muscle 2 wk after glycerol injection and analysis of relative IMAT area and adipocyte count. (Scale bar, 0.5 mm, Top; 100 µm, Bottom.) (G) Sparc, (H) Fabp4, and (I) Pparg expression in AAV-Sparc–infected tibialis anterior muscle 2 wk after glycerol injection (n = 6 versus 6 versus 5). qPCR values were normalized to 18S rRNA. All data are plotted as mean ± SEM. Significance was evaluated by (B–F and J) two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test and (G–I) one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001.