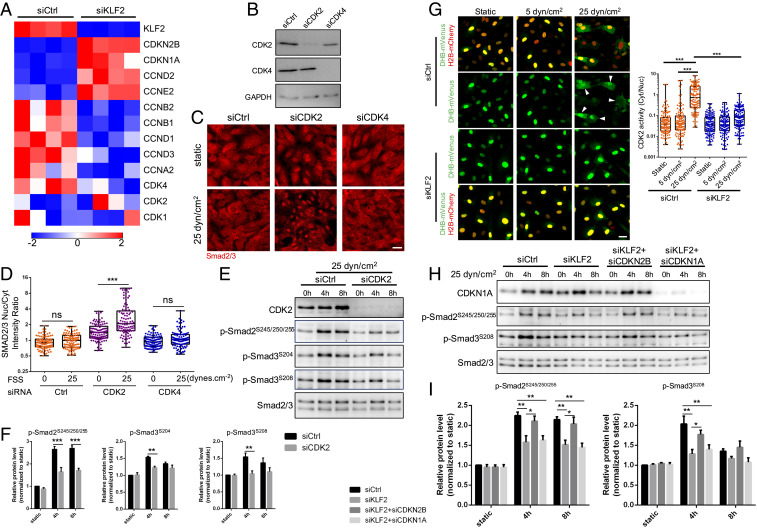
Fig. 7.
CDK2 mediates Smad2/3 inhibition at high FSS. (A) Heat map for the expression of cell cycle regulators after Klf2 KD; n = 4 samples in each group. Color key shows log2 change after Klf2 depletion. (B) Western blot confirming CDK2 and CDK4 KD efficiency. (C) Representative Smad2/3 staining under static and 25 dynes/cm2 FSS in HUVECs treated with Ctrl, CDK2, or CDK4 siRNA. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (D) Quantification of Smad2/3 nucleus/cytoplasm intensity ratio. n = 100 to 150 cells for each group from three independent experiments. (E) Representative Western blot of indicated Smad2/3 linker phosphorylation in HUVECs treated with Ctrl and CDK2 siRNA under high (25 dynes/cm2) FSS at indicated time points. (F) Densitometric quantification of indicated Smad2/3 linker phosphorylation; n = 3 independent experiments. Data represent mean ± SEM. (G) To assay Cdk2 activity, cells were cotransfected with the DHB-venus biosensor and histone 2B (H2B)-mCherry to mark the nuclei. Active Cdk2 phosphorylates the DHB moiety, leading to its nuclear export. Cells were subjected to FSS for 6 h at 5 or 25 dynes/cm2, as indicated, then fixed and images taken. Ratio of cytoplasmic/nuclear signal was quantified and graphed. (Left) Representative images of DHB-mVenous and H2B-mCherry in HUVECs treated with control or KLF2 siRNA. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) Arrowheads are CDK2 high-activity cells. (Right) Quantification of CDK2 activity (cytoplasm/nucleus intensity ratio). n = 120 cells for each group from three independent experiments. (H) Representative Western blot of indicated Smad2/3 linker phosphorylation in HUVECs treated with Ctrl, KLF2, KLF2 plus CDKN2B, and KLF2 plus CDKN1A siRNA under high (25 dynes/cm2) FSS at indicated time points. (I) Densitometric quantification of indicated Smad2/3 linker phosphorylation; n = 3 independent experiments. Data represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ns: not significant, calculated by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison tests (D and G) and two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison tests (F and I).