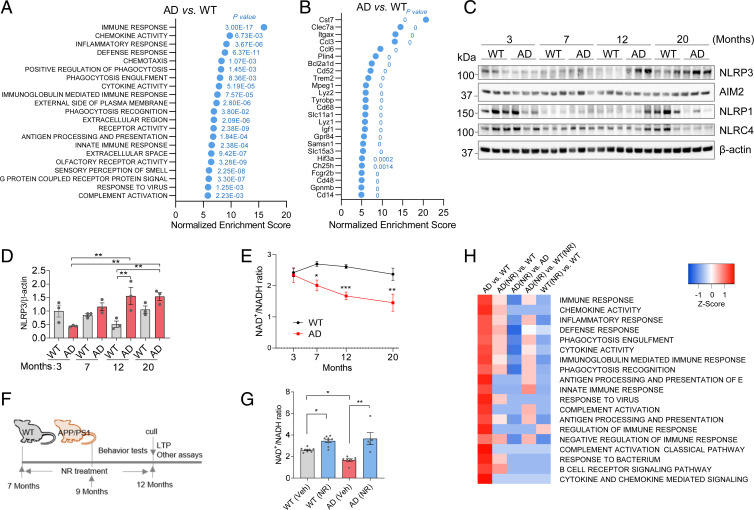
Fig. 1.
Neuroinflammation is associated with reduced NAD+ levels during aging in AD mice. (A) GO term analysis of gene expression microarray from hippocampi. The most changed terms in AD compared to WT hippocampus are shown. P values for each significant changed pathway are shown. (B) The most changed genes from hippocampi microarray of AD compared to WT. P values for each significant changed gene are shown. (C) Western blots of specific inflammation-related proteins at different ages from cortical tissue from WT and APP/PS1 mice. n = 3 mice per group. (D) Quantification of NLRP3 protein level in C. (E) NAD+/NADH ratio in different ages of AD and WT mouse cortex. n = 3 to 8 mice per group. (F) Experimental design. The 7-mo-old AD and WT mice were treated with NR (12 mM) in their drinking water or vehicle for 5 mo. Behavioral tests were performed after 2 mo NR treatment. Mice were culled after 5 mo on NR or vehicle treatment for downstream assays. (G) NAD+/NADH ratio in 12-mo-old AD and WT mouse cortex with or without NR treatment. n = 5 to 9 mice per group. (H) Microarray heatmap showing significantly changed inflammation-related pathways in NR- or vehicle-treated AD or WT mice hippocampus. Data: mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was performed with two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test compared with control. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.