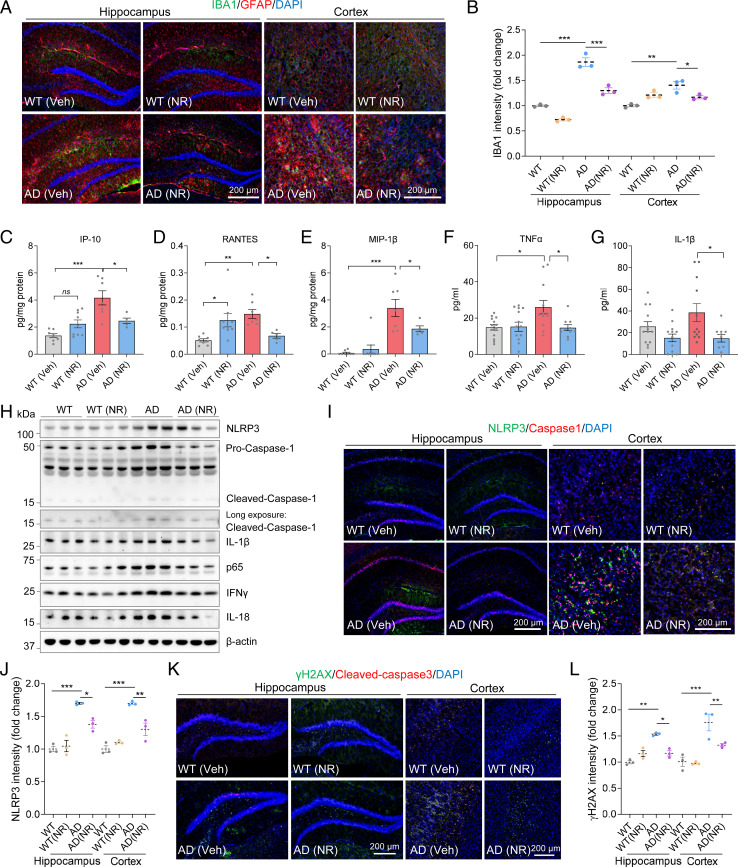
Fig. 2.
NR decreases neuroinflammation, the NLRP3 inflammasome, NF-κB, and DNA damage. (A) Representative immunostaining images of IBA1 (green) and GFAP (red) with DAPI (blue) in mouse hippocampi and cortex. (B) Quantification of IBA1 intensity in A. n = 3 mice per group. (C–E) Proinflammatory cytokines or chemokines IP-10 (C), RANTES (D), and MIP-1β (E) levels detected by cytokine array in AD or WT mice cortex with or without NR treatment. n = 5 to 9 mice per group. (F and G) Proinflammatory cytokines or chemokines TNF-α (F) and IL-1β (G) levels detected by cytokine array in AD or WT mice plasma with or without NR treatment. n = 10 to 14 mice per group. (H) Western blots of specified proteins in WT and AD mice cortex with or without NR treatment. n = 3 mice per group. (I) Representative immunostaining images of NLRP3 (green) and caspase-1 (red) with DAPI (blue) in mice hippocampi and cortex. (J) Quantification of NLRP3 intensity in I. n = 3 mice per group. (K) Representative immunostaining images of γ-H2AX (green) and Cleaved-caspase-3 (red) with DAPI (blue) in mice hippocampi and cortex. (L) Quantification of γ-H2AX intensity in K. n = 3 mice per group. Data: mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was performed with two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s or Bonferroni multiple comparisons test compared with control. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.