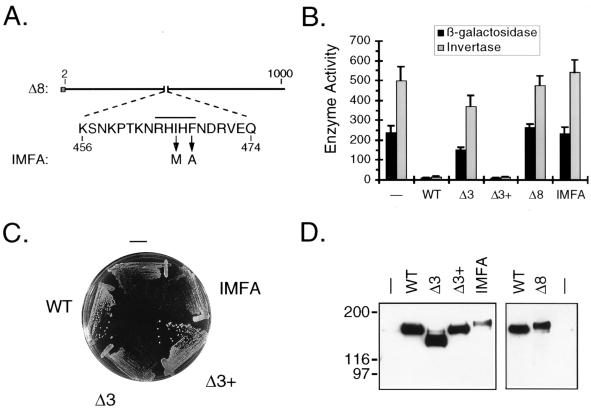
FIG. 2.
Analysis of PP1-binding site mutants. (A) Diagram of the Δ8 and IMFA derivatives of Reg1. The amino acid sequence presented is that which is deleted in the Δ8 construct. The overline indicates the position of the putative PP1-binding sequence. Arrows indicate the amino acid substitutions introduced to create the IMFA construct. (B) Analysis of ADH2 and SUC2 expression. KDY82 cells transformed with either pRS316 (−), pKD89 (WT), pKD95 (Δ3), pKD115 (Δ3+), pKD104 (Δ8), or pKD114 (IMFA) were grown in synthetic selective broth containing 5% glucose. ADH2 expression was assayed as β-galactosidase activity (in Miller units) expressed from the integrated ADH2 reporter plasmid YIp23ADH2-lacZ. Each measurement represents the mean for six independent transformants, and error bars represent the standard deviation. SUC2 expression was assayed as invertase activity (in nanomoles of sucrose hydrolyzed per min per 107 cells). A single transformant having β-galactosidase activity nearest the average was assayed in triplicate. (C) Effect of PP1-binding site mutations on growth. Transformants were streaked to single colonies on SM agar lacking uracil and containing 2% glucose. The agar plate was incubated for 2 days before being photographed. (D) Western blot analysis of binding site mutants. Protein blots of KDY82 transformants were prepared and analyzed as described in the legend for Fig. 1B. The right panel was exposed to X-ray film for a fivefold longer period of time than the left panel. WT, wild type.