Figure 1.
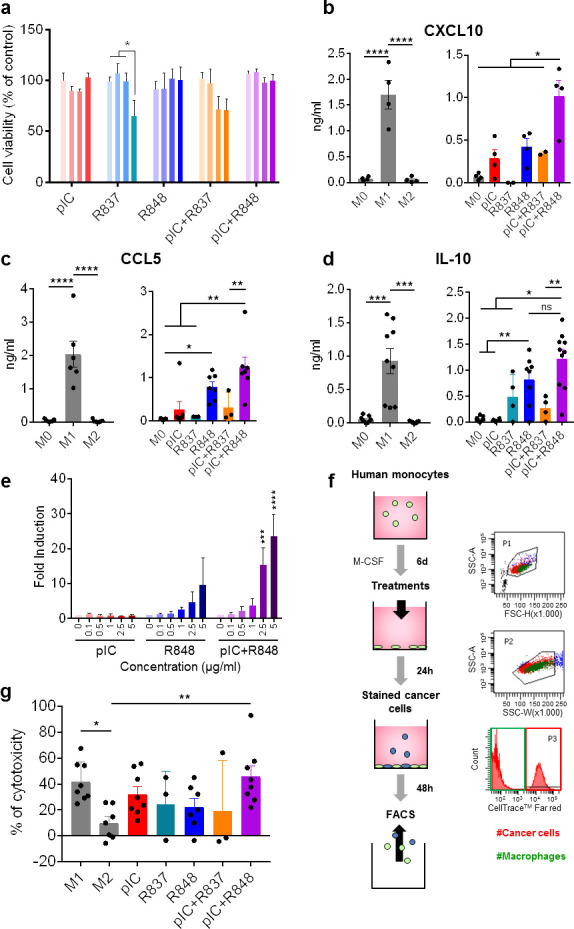
Toxicological and immunomodulatory evaluation in vitro of intracellular TLR agonists alone or combined using primary human macrophages. Macrophages were in vitro differentiated from purified monocytes stimulated with 25 ng/mL of recombinant human macrophage colony-stimulating factor for 6 days (M0); M1 and M2 polarized macrophages were obtained by stimulation with 100 ng/mL of lipopolysaccharide+50 ng/mL of interferon-γ or 20 ng/mL of IL-4, respectively, for 24 hours. (A) Cell viability (Alamar blue) of M0 macrophages exposed 24 hours to TLR agonists alone or in different combinations. concentrations used were 5, 10, 20 and 50 µg/mL, represented by color gradient from left to right. (B–D) cytokine secretion (ELISA) of (B) CXCL10, (C) CCL5, and (D) IL-10 by macrophages exposed for 24 hours to 5 µg/mL of TLR agonists or untreated M0 macrophages. In each panel, M1 and M2 polarized macrophages from the same individuals are shown as reference populations. Each dot corresponds to macrophages from each blood donor. (E) THP-1-Lucia cells for monitoring the NF-kB signal transduction pathway were exposed for 16 hours to pIC and/or R848 at indicated concentrations. Bars represent mean±SD, n=3. (F, G) Cytotoxic activity of TLR-treated macrophages toward human Panc1 cancer cells stained with CellTrace. Each dot corresponds to macrophages from each blood donor. Bars represent mean±SEM. Statistical comparison was performed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Statistically significant differences are represented as follows: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and ****p<0.001. IL, interleukin; NF-kB, nuclear factor-kappa B; ns, non-significant; pIC, poly(I:C); R837, imiquimod; R848, resiquimod; TLR, toll-like receptor.
