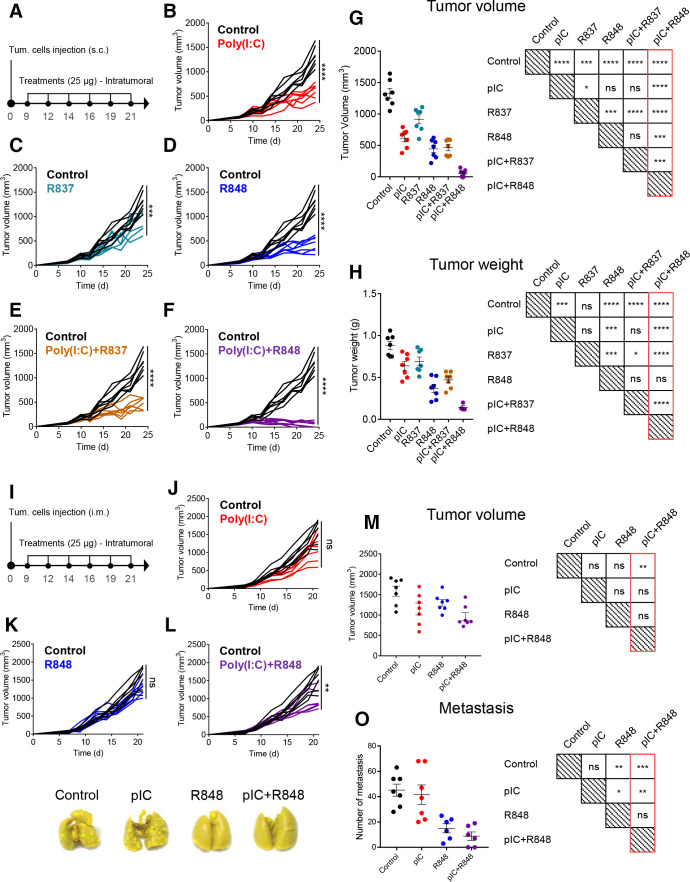
Figure 2.
antitumoral and antimetastatic efficacy of intratumoral injections of pIC, R837 and R848, alone or combined, in the immunocompetent lung cancer murine model CMT167 and fibrosarcoma murine model MN/MCA1. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental protocol. CMT167 cells were injected subcutaneously in the flank. From day 9 to day 21, mice received 6 intratumoral injections of TLR agonists (25 µg) as monotherapy or in combination. Control mice received only saline. (B–F) Evolution of tumor growth of mice treated with (B) pIC, (C) R837, (D) R848, (E) combination of pIC+R837, and (F) combination of pIC+R848. (G) Comparison of tumor volume and (H) tumor weight at sacrifice and graphical visualization of the statistical differences (right). Representative experiment of two performed. (I) Schematic representation of the experimental protocol. MN/MCA1 cells were injected intramuscularly in the thigh. From day 9 to day 21, mice received six intratumoral injections of pIC and R848 (25 µg) as monotherapy or in combination. Control mice received only saline. (J–L) Evolution of tumor growth in mice treated with (J) pIC, (K) R848, or (L) pIC+R848. (M) Comparison of tumor volume and (N) the number of surface lung macrometastasis at sacrifice and graphical visualization of the statistical differences (right). (O) Representative pictures of lungs from each treatment group. Bars represent mean±SEM, n=7 per group. Statistical comparison was performed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Statistically significant differences are represented as follows: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and ****p<0.001 vs control. ns, non-significant; pIC, poly(I:C); R837, imiquimod; R848, resiquimod; TLR, toll-like receptor.