Figure 2. ArlRS and MgrA control formation and immune evasion of model in vitro S. aureus abscess communities.
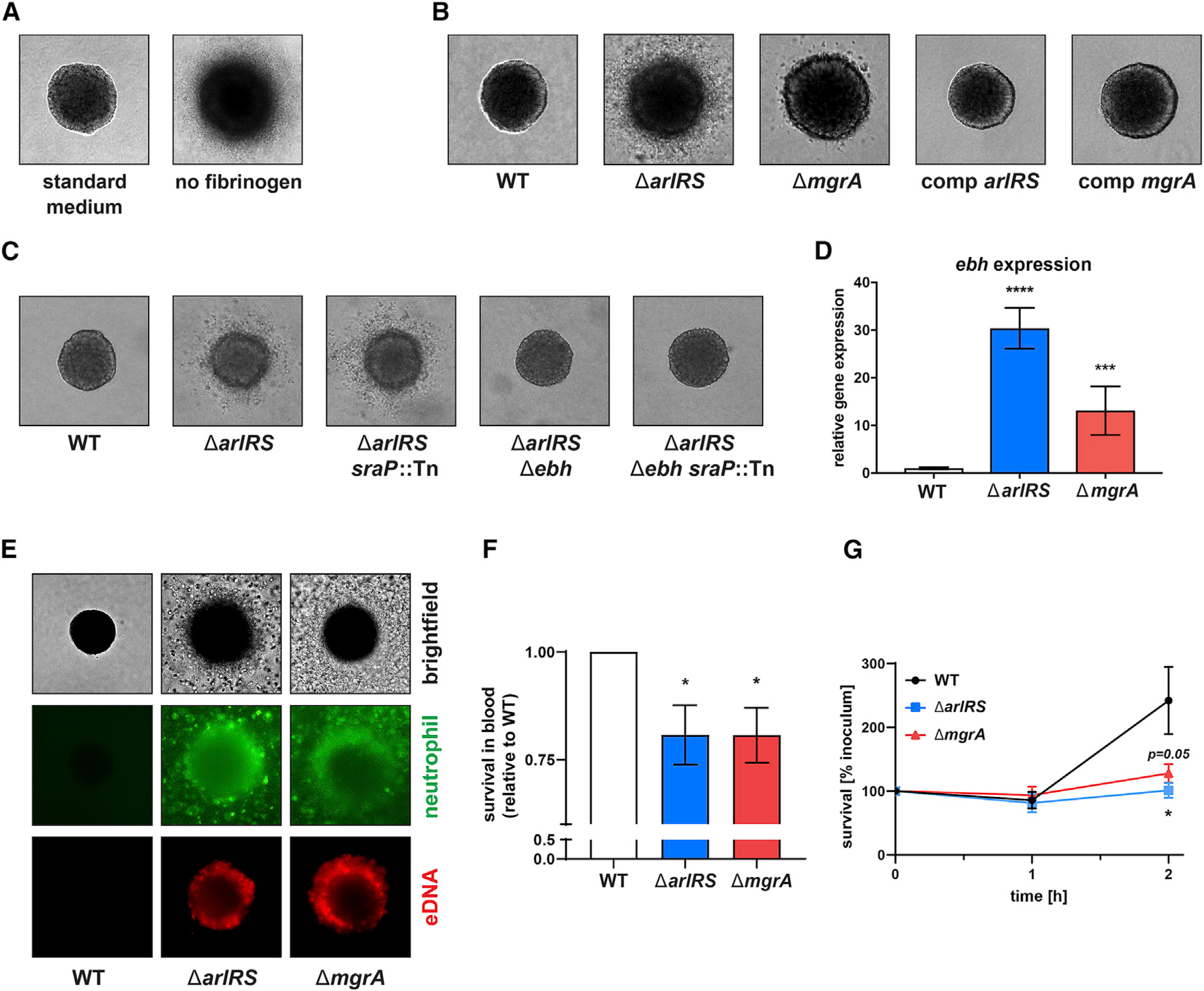
(A–C) Three-dimensional SACs formed from individual S. aureus cells after culturing in collagen/fibrinogen/RPMI gels for 16 h. These were used to determine the role of fibrinogen present in the culture medium (A), the effects of mutations in the ArlRS-MgrA signaling system (B), and the role of giant surface proteins SraP and Ebh in causing the starburst phenotype in the ΔarlRS mutant strains (C).
(D) Expression of ebh in mid-exponential S. aureus RPMI culture was measured with qPCR and normalized to gyrB expression.
(E) Behavior of human neutrophils (stained green with CFDA-SE) 3 h after addition to the in vitro three-dimensional abscess models was also visualized, with propidium iodide (PI) added before imaging to stain extracellular DNA and lysed cells.
(F) Survival of S. aureus after 1-h incubation with fresh human blood was quantified and normalized to WT survival.
(G) Survival of S. aureus co-incubated with purified human neutrophils was measured.
Representative images are shown. Image size: 350 × 350 μm. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. n = 6 (D and F) or 5 (G). *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. All p values are for comparisons to WT. See also Figures S2–S4.
