Graphical Abstract.
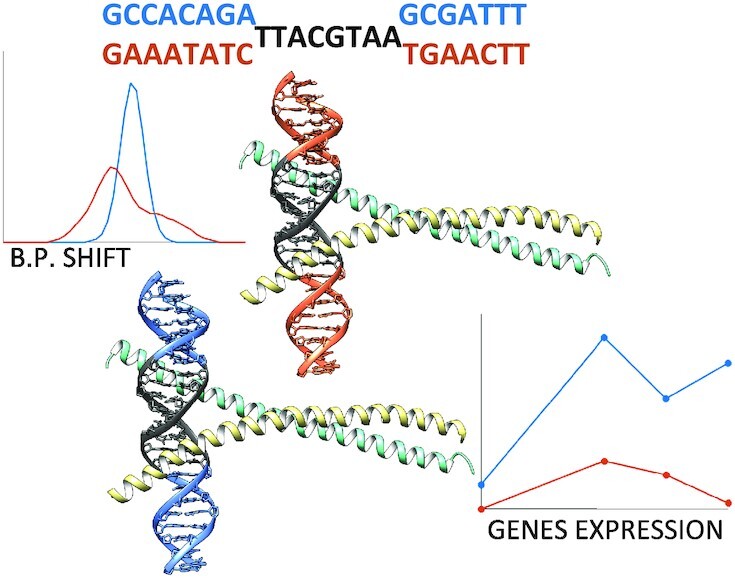
Activator proteins 1 (AP-1) comprise one of the largest families of eukaryotic basic leucine zipper transcription factors (TFs). We show that Ap1 TFs exploit the sequence-specific flexibility of DNA within the response element to form stable protein–DNA complexes. The complex stability also depends on the four to six nucleotides, flanking AP-1 response elements. Bioinformatics analysis of differential expression of the studied genes supports our conclusions: the stability of protein–DNA complexes, modulated by the flanking environment, influences the gene expression levels.
