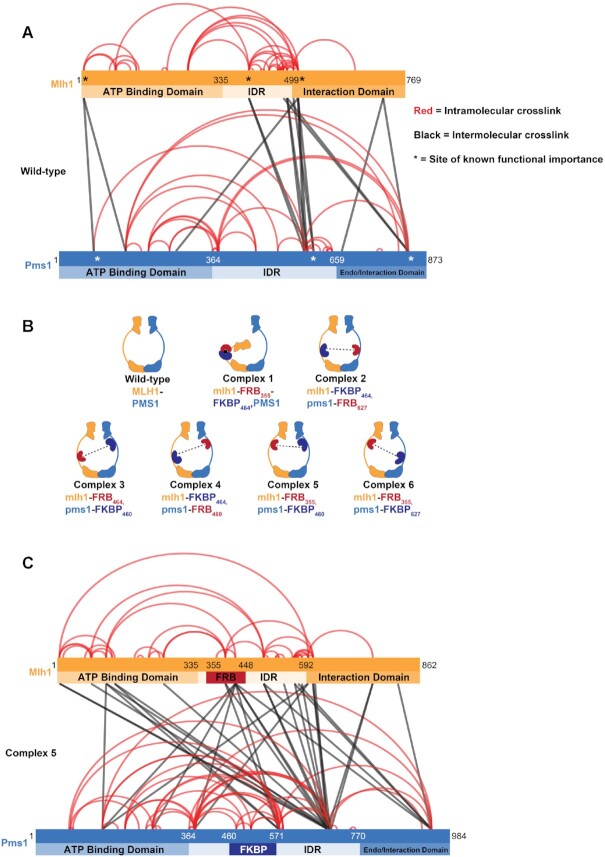
Figure 2.
Crosslinking mass spectrometry of Mlh1–Pms1 identifies IDR regions that display limited or extensive interactions within a subunit or with the other subunits. (A) Mlh1–Pms1 was crosslinked with DSSO and then subjected to cross-linking mass spectrometry (XL-MS; Materials and Methods; Supplementary Table S3). The positions for each domain are shown. For Mlh1, the ATP binding domain extends from aa position 1-335; the IDR from 336–498; and the interaction domain from 499–769. For Pms1 the ATP binding domain extends from aa position 1-364; the IDR from 365–659; and the endonuclease/interaction domain from 660–873. Shown are the inter- and intra-subunit lysine residue crosslinks with respect to the ATP binding, IDR, and endonuclease/interaction domains of Mlh1 and Pms1. Crosslinks involving the same positions (indicated by the density of the line) were seen multiple times in a single experiment and were also identified in a repeat experiment. For simplicity, we show the composite of the results from two independent crosslink trials. * Represent positions in Mlh1 and Pms1 shown previously to disrupt MMR. (B) Cartoons of Complexes 1 to 6 analyzed in this study. Crosslinking analysis and previous deletion analysis of Mlh1 and Pms1 IDRs (23; Supplementary Figure S1A) encouraged is to insert FRB and FKBP domains into the IDRs of Mlh1 and Pms1 at amino acid positions 355 or 464 in Mlh1 or 460 or 627 in Pms1, with the specific insertion sites of the FRB and FKBP domains in Complexes 1 to 6 indicated. Potential interactions with rapamycin are indicated by the dotted black lines. (C) XL-MS analysis of Complex #5 (mlh1-FRB355, pms1-FKBP460) with the insertions of FRB and FKBP indicated. The positions of each domain are shown but are shifted by 97 amino acids in Mlh1 with the insertion of FRB (93 amino acids plus four spacer amino acids), and 111 amino acids in Pms1 for the insertion of FKBP (107 amino acids plus four spacer amino acids).