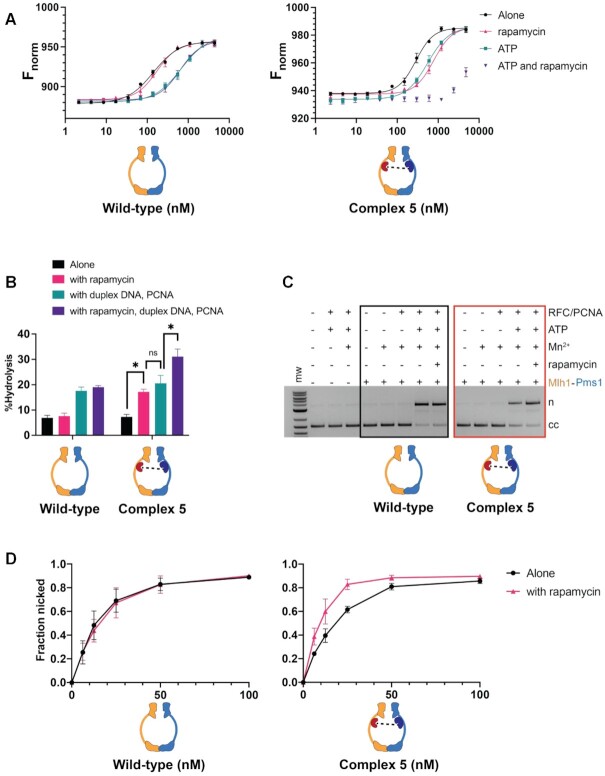
Figure 3.
Complex #5 (mlh1-FRB355, pms1-FKBP460) displays defective DNA binding but enhanced ATP hydrolysis and endonuclease activity in the presence of rapamycin. (A) MST analysis of Mlh1–Pms1 and Complex #5 in the presence and absence of 49 bp homoduplex DNA (20 nM), ATP (1 mM) and rapamycin (1 μM). Three independent experiments (error bars indicate the mean ± standard deviation) and were performed using at least two independently purified batches of each protein. Fnorm was calculated by dividing Fhot (average fluorescence value in the heated state) by Fcold (average fluorescence value measured in the cold state before the infrared laser is turned on) and plotted as parts per thousand (%). See Materials and Methods for details. (B) ATP hydrolysis activities of Mlh1–Pms1 and Complex #5 (0.40 μM each) were determined in the presence and absence of PCNA (0.250 μM), 49-bp homoduplex DNA (0.75 μM), and rapamycin (1 μM). Error bars indicate ± one standard deviation for three replicates. * denotes statistical significance in a Student's t-test between the indicated comparisons; ns indicates not significant. (C) Endonuclease activities of Mlh1–Pms1 and Complex #5 (50 nM each) determined on a closed circular DNA substrate (cc) in the presence (+) or absence (−) of MnSO4, ATP, rapamycin, and yeast PCNA/RFC (Materials and Methods). MnSO4, ATP, rapamycin, RFC and PCNA were included at 5 mM, 0.5 mM, 1 μM, 125 nM and 250 nM, respectively. n = nicked product. (D) Endonuclease activities were determined at the indicated concentrations of wild-type and Complex #5. Assays were performed in the presence of MnSO4, ATP, RFC, PCNA. Rapamycin was included as indicated. Error-bars indicate the standard deviation of three replicates (Supplementary Figure S3).