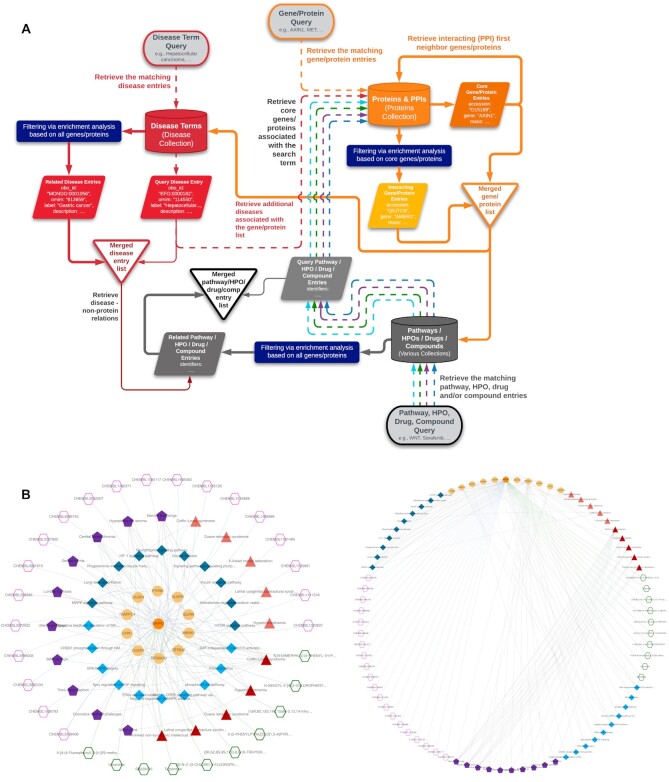
Figure 3.
(A) Simplified workflow of the knowledge graph construction procedure, explained over an example disease term query. With the initiation of graph construction by a disease query, the system: (1) finds the matching disease entry from the relevant collection, (2) gathers genes/proteins that are associated with the query disease (i.e. core genes/proteins), (3) collects additional genes/proteins (i.e. first-neighbours) using PPIs of core genes/proteins, (4) identifies biological processes (pathways), of which these genes/proteins (core + neighbouring) are members, (5) gathers phenotypic terms (HPO) associated with the whole gene/protein set, (6) obtains known drugs and drug candidate compounds targeting these genes/proteins, together with our deep-learning-based interaction predictions and (7) revisits the disease collection to make another query with all collected genes/proteins, to obtain the disease entries that have similar implications as the query disease. The Full-scale workflow of the CROssBAR knowledge graph construction process is provided in Supplementary Figure S1; (B) an example KG obtained from CROssBAR-WS, generated on-the-fly with the user's query of ‘MAPK1’ gene (with the node limit of 10 for each biomedical/biological component, and other default parameters), displayed under the layout selections of multi-layered CROssBAR (left) and circular (right).