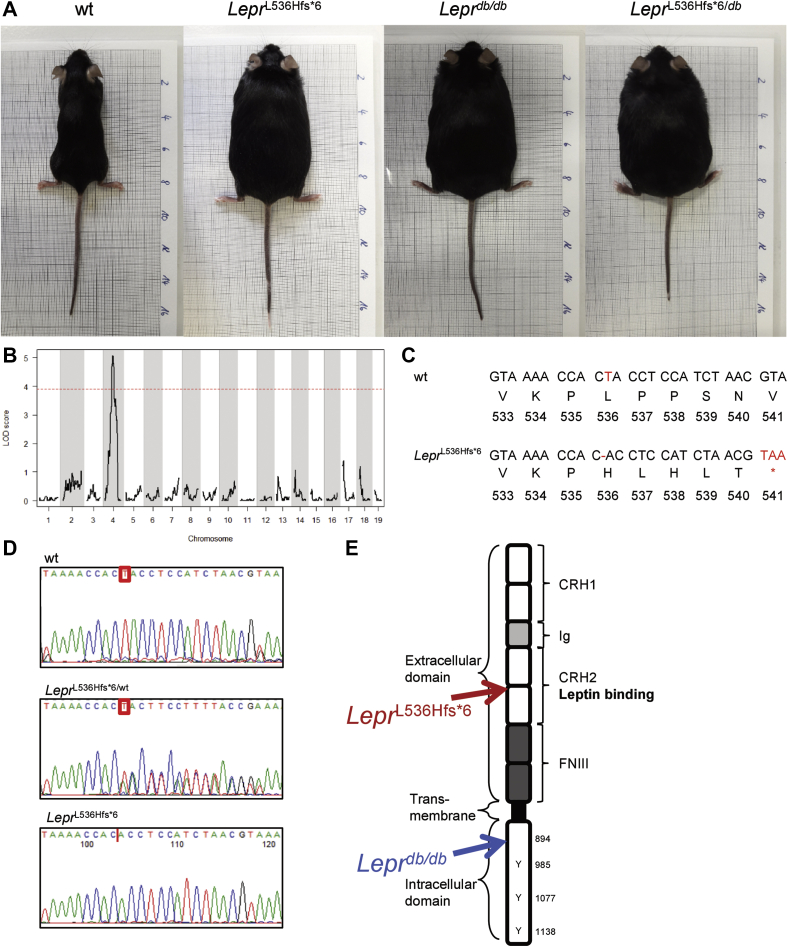
Fig. 1.
QTL analysis and LeprL536Hfs*6 mutation. A: Pictures of 12-week-old female mice on mm scale. B: Quantitative trait locus (QTL) identification on chromosome 4 with R/qtl using Haley Knott regression (37). C: Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the QTL region on chromosome 4 resulted in the identification of the point mutation at position 536 causing the novel LeprL536Hfs*6 spontaneous Lepr mutant mice. The mutation results in a deletion in exon 11 which leads to a frame shift and stop codon within the next 5 aa. D: Exemplary sequence of a wt, a heterozygous LeprL536Hfs*6/wt, and a homozygous LeprL536Hfs*6 mouse. F: Schematic representation of the Lepr protein with highlighted positions for LeprL536Hfs*6 and Leprdb/db mutations as well as cytokine receptor homology (CRH1/2), Immunoglobulin domain (Ig), fibronectin III domain (FNIII).