Figure 1.
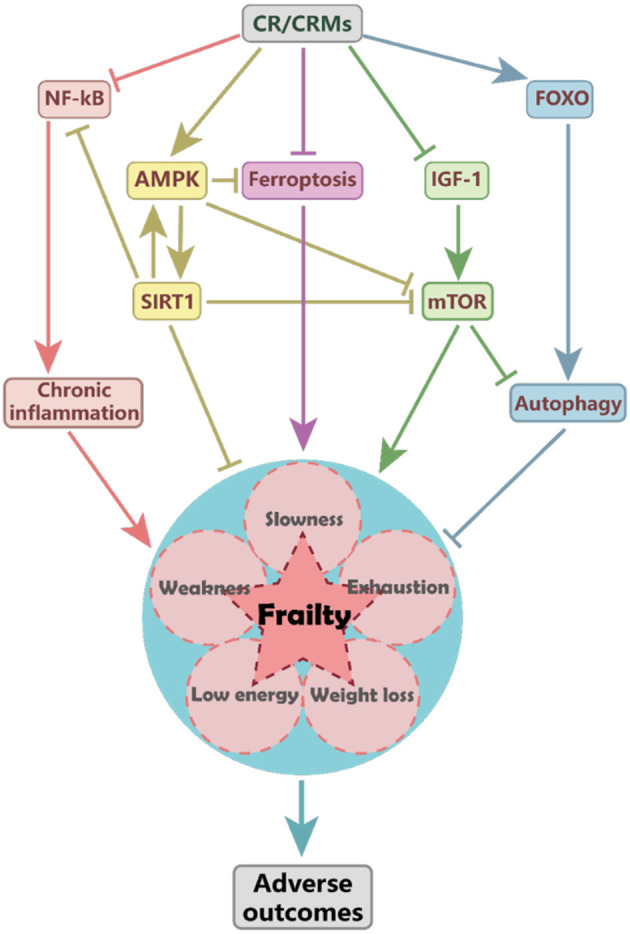
The proposed mechanism of caloric restriction (CR) impacts frailty. CR may reduce the risk of frailty and associated adverse outcomes by activating the AMPK and SIRT1 pathways, inhibiting the IGF-1 and mTOR signaling and ferroptosis, and reducing the inflammation mediated by NF-KB pathways. CR-induced SIRT1 activation may upregulate AMPK and suppress NF-κB and mTOR activity. CR and metformin may attenuate ferroptosis by activating the AMPK pathway and improving frailty. AMPK, adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase; CR, caloric restriction; CRMs, caloric restriction mimetics; FOXO, forkhead box O; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; SIRT1, silent mating-type information regulation 2 homolog 1.
