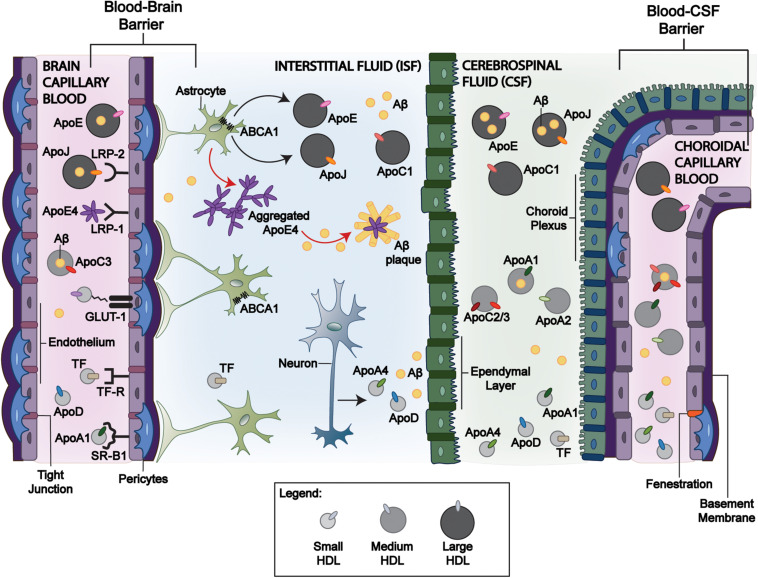
FIGURE 1.
Mechanisms of HDL-P transport across blood-brain interfaces and its relevance to Aβ clearance. Circulating large apoE, apoJ, and apoC-III containing HDL-P facilitate Aβ efflux across the BBB and BCSFB through various receptor-mediated interactions and can promote Aβ efflux from the brain despite a limited BBB exchange. Of the apoE isoforms, apoE4 has the greatest affinity to LRP-1 that may allow greater BBB transport. While larger HDL-P have limited brain delivery, smaller HDL-P may exchange among the blood, CSF, and interstitial fluid compartments. ApoJ has been demonstrated to interact with LRP-2 at the BBB and BCSFB for Aβ clearance, but lipidated apoJ and apoE3 have limited brain delivery from the periphery. While peripheral apoA-I and apoA-II cross the BCSFB and are present in CSF, the size/shape that promote this exchange remains unclear. Astrocyte-derived apoJ and apoE undergo lipidation by ABCA1. In comparison to apoE2 and apoE3, apoE4 has inefficient interactions with ABCA1 (red arrow). It remains lipid-poor and is more prone to aggregation, promoting Aβ plaque formation. In contrast, the greater lipidation of apoE2 and apoE3 compared to apoE4 by ABCA1 limits the formation of Aβ plaques. LRP-1: Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1; LRP-2: Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 2; ABCA1: ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily A Member 1. Blood-Brain Barrier: BBB, and Blood-CSF Barrier: BCSFB.