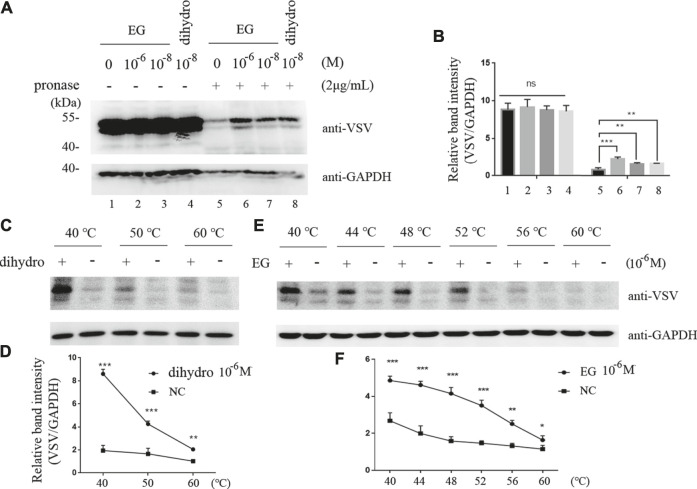
FIGURE 2.
EG interaction with 5-HT1B in DARTS and CETSA experiments. (A,B) Intact Flp-In™ T-REx™ 293 cells stably induced to express mGluR5-VSV-G-5-HT1B were treated with EG or dihydro (dihydroergotamine, a 5-HT1B agonist) at indicated concentrations and lysates were subjected to pronase (2 μg/ml) digestion. 5-HT1B protein with EG and dihydro protection in pronase digestion detected by western blotting and enrichment of 5-HT1B protein in pronase-induced depletion quantified by relative band intensity compared with GAPDH. (C,D) Intact Flp-In™ T-REx™ 293 cells of stably expressing mGluR5-VSV-G-5-HT1B treated with dihydro compared to control cells. The harvested cells were lysed three times by alternate freezing and thawing with liquid nitrogen before heating to the indicated temperatures. The 5-HT1B engagement with dihydro was detected by western blotting and quantified by relative band intensity compared with GAPDH. The corresponding 5-HT1B thermodynamic stabilization curves distinguish the treated from non-treated cells. (E,F) Stable cells expressing mGluR5-VSV-G-5-HT1B treated with EG compared to control cells. The cells were alternately frozen and thawed three times followed by heating to the indicated temperatures, and the 5-HT1B engagement with EG was detected by western blotting. The corresponding 5-HT1B thermodynamic stabilization curves distinguished the treated from non-treated cells. The mean values (±S.D.) of three independent experiments are shown. An asterisk indicates statistical significance (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.001, ***p<<0.001).