FIGURE 4.
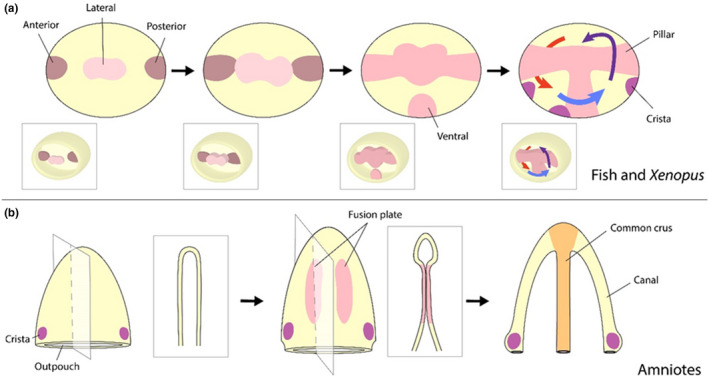
Semi‐circular canal morphogenesis. The cells that give rise to the canals originate in a lateral region adjacent to the presumptive cristae. However, there are variations between how these canals form in anamniotes, such as zebrafish and Xenopus, and amniotes, such as mouse and chick. (a) Canal formation in zebrafish and Xenopus begins with an outgrowth of projections that bulge inward into the otic vesicle. When these projections fuse, they become the pillars around which the canals are formed. (b) In amniotes, the canals are sculpted from two out‐pouches, one ventral (shown above) and one horizontal. Fusion plates are formed by opposing epithelium that extend toward one another. Following fusion, these plates are resorbed through apoptosis. In the above example, this process forms the anterior and posterior canals, with the common crux situated between them
