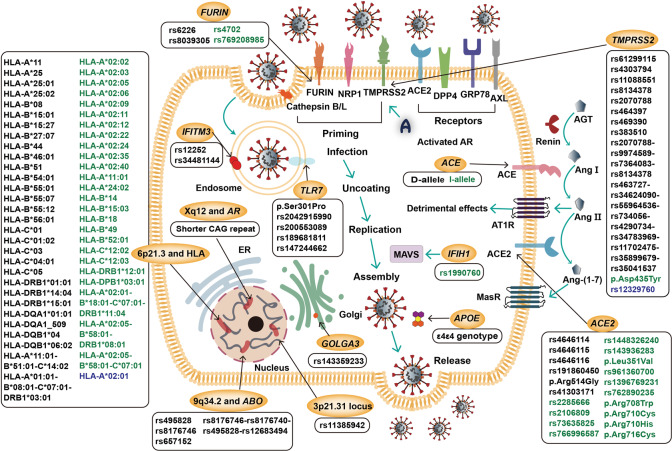
Fig. 1.
Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 and genetic variants associated with COVID-19. After the recognition of ACE2, DPP4, GRP78, and AXL receptors and the priming by TMPRSS2, FURIN, and NRP1, as well as cathepsin B/L, SARS-CoV-2 enters cells and starts the replication process to assemble and release. Activated AR induces TMPRSS2 expression. ACE/Ang II/AT1R and ACE2/Ang-(1–7)/MasR axes regulate RAAS to involve in COVID-19. The risk (black), protective (green), and uncertain (blue) variants or alleles or haplotypes for COVID-19 are highlighted. SARS-CoV-2 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, COVID-19 coronavirus disease 2019, ACE2 angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, DPP4 dipeptidyl peptidase 4, GRP78 glucose-regulated protein-78, AXL anexelekto, TMPRSS2 transmembrane protease serine 2, FURIN furin, paired basic amino acid-cleaving enzyme, NRP1 neuropilin-1, AR androgen receptor, AGT angiotensinogen, Ang angiotensin, ACE angiotensin-converting enzyme, AT1R angiotensin II type 1 receptor, MasR Mas receptor, TLR7 the Toll-like receptor 7 gene, IFITM3 the interferon induced transmembrane protein 3 gene, HLA human leukocyte antigen, GOLGA3 the golgin A3 gene, ABO the ABO, alpha 1–3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase and alpha 1–3-galactosyltransferase gene, APOE the apolipoprotein E gene, IFIH1 the interferon induced with helicase C domain 1 gene, MAVS mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein, ER endoplasmic reticulum