FIGURE 3.
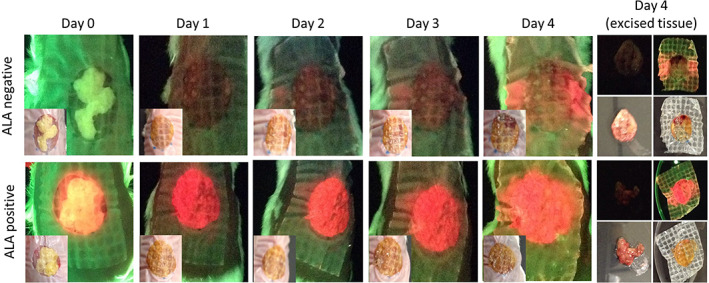
In vivo detection of fluorescence from bacteria within biofilms. Wounds were inoculated with polymicrobial biofilms grown in the absence of δ‐aminolevulinic acid (ALA) (ALA negative, n = 12). As a positive control, a subset of wounds were inoculated with biofilm grown in the presence of supraphysiological levels of ALA (ALA positive, n = 3). Standard (inset) and fluorescence images were captured daily from Days 0 to 4. Red fluorescence in the ALA negative group was evident on fluorescence images by Day 1, and fluorescent signal intensified up to Day 4 when wounds were excised, washed, and reimaged. Compared with Day 4 in vivo fluorescent signals, red fluorescent signal from excised wound bed material was decreased, much of which was because of a portion of the biofilm biomass being retained on the bandage
