Fig. 1 |. Single-cell multi-omics for deciphering clonal evolution in cancer.
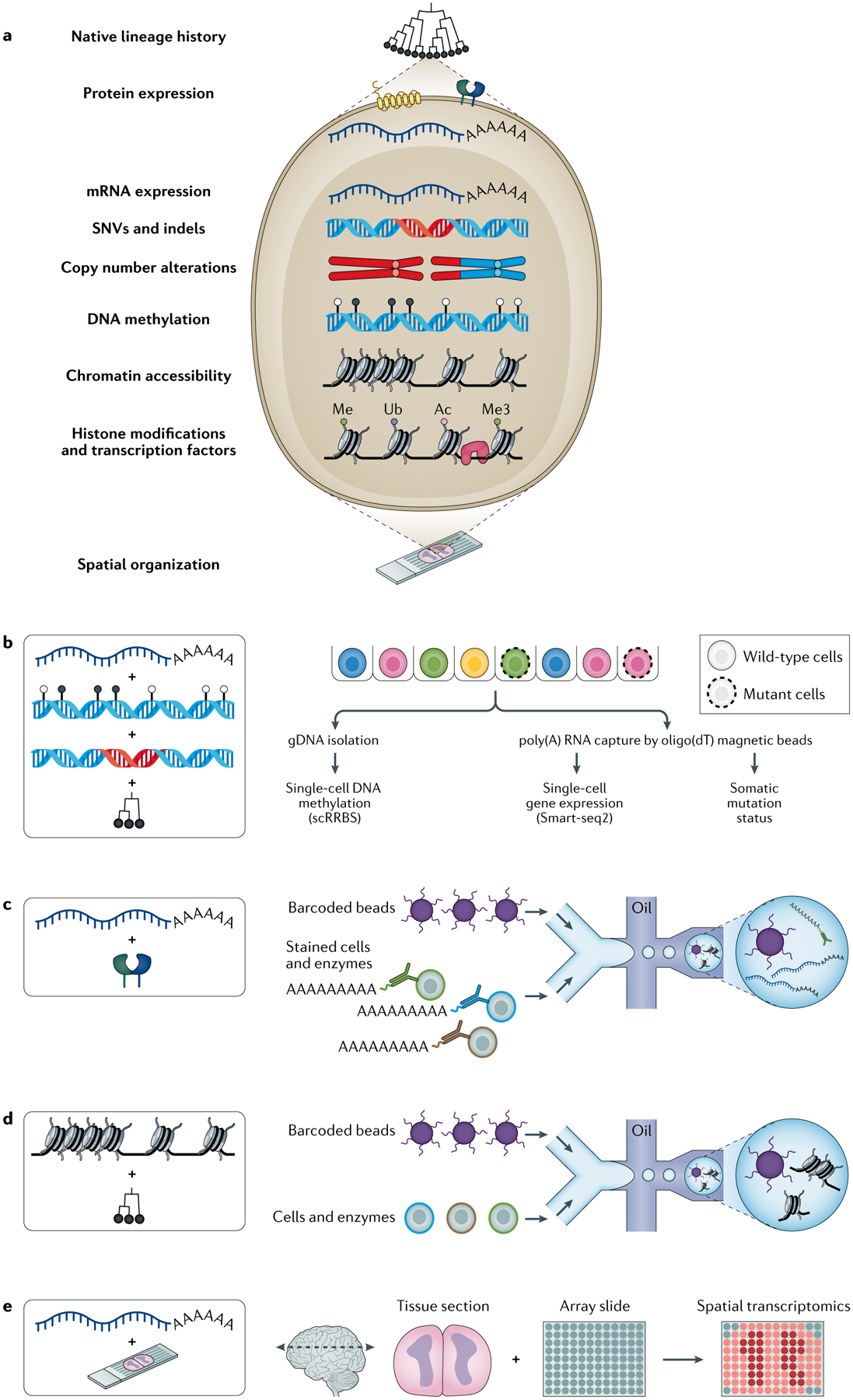
Analytic or experimental integrations of multiple data ‘omics’ modalities in single-cells advance our understanding of mechanisms of clonal evolution. a | Cancer cell representation with heritable traits that can be interrogated via multi-omics platforms. b | Extracting DNA methylation (DNAme) and transcriptomic information from the same cells experimentally has been achieved by modifying plate-based single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) protocols (for example, Smart-seq2), in which both RNA and DNA are respectively isolated from the same cells for whole-transcriptome and DNAme data through bisulfite sequencing121,128,129. Heritable stochastic DNAme changes can then be exploited as native barcodes to directly infer the high-resolution phylogenetic history of tumour cells121. c | scRNA-seq with integration of protein expression measurements can be performed in parallel for the same cells122,123. DNA-barcoded antibodies, acting as synthetic transcripts, are used to convert the detection of proteins into a quantitative readout. This allows the immunophenotyping of cells to be integrated with an unbiased transcriptome analysis using existing single-cell sequencing approaches. d | High-sensitivity somatic genotyping in which, for instance, any mutation in mitochondrial DNA may serve as lineage markers. Interrogating these naturally occurring genetic barcodes within scATAC-seq97 (or scRNA-seq) provides high-resolution phylogenies coupled with cell state information. e | As an example of spatially aware platforms160,162–164,166,169, spatial transcriptomics165 utilizes molecular barcodes for the detection of mRNA molecules and maps them to their spatial positioning. gDNA, genomic DNA; indels, insertions or deletions; scRRBS, single-cell reduced-representation bisulfite sequencing; SNVs, single nucleotide variants.
