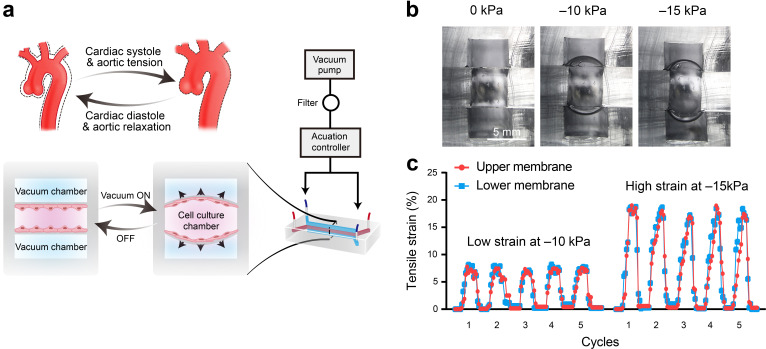
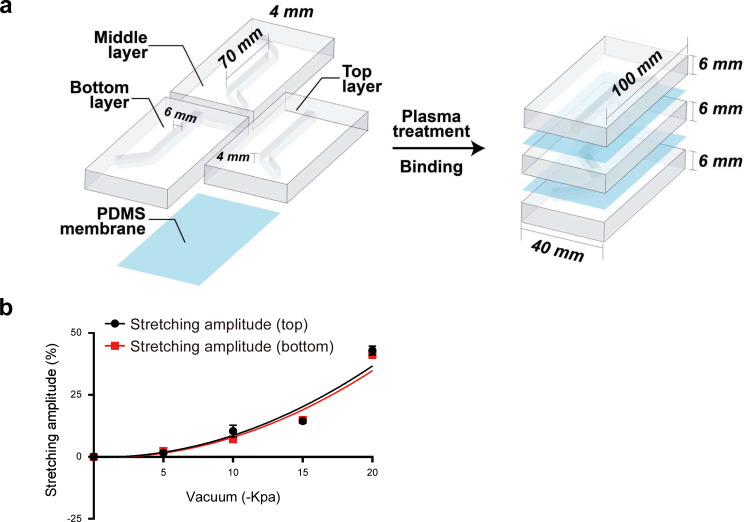
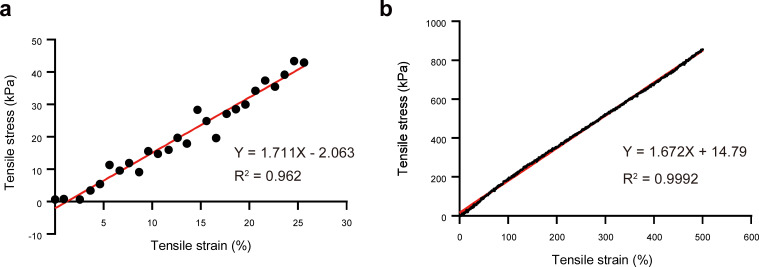
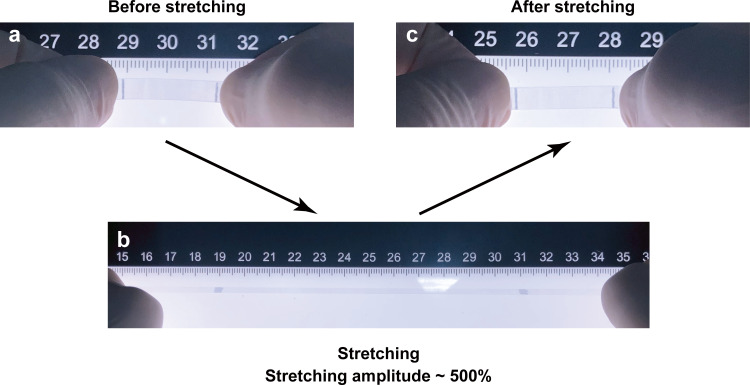
Figure 2. Schematic design and strain characterization of the aorta smooth muscle-on-a-chip model.
(a) Schematic overview of the in vitro chip model. (b) Cross-sectional view of the microfluidic aorta smooth muscle-on-a-chip model showing the deformations of the PDMS membranes under different vacuum pressures. The scale bar represents 5 mm. (c) Measured tensile strains of the upper (red) and lower (blue) membranes at negative pressures of 10 kPa and 15 kPa for five cycles. The peak tensile strain per cycle averaged 7.18 ± 0.44% with a cyclic negative pressure of 10 kPa and 17.28 ± 0.91% with a cyclic negative pressure of 15 kPa.