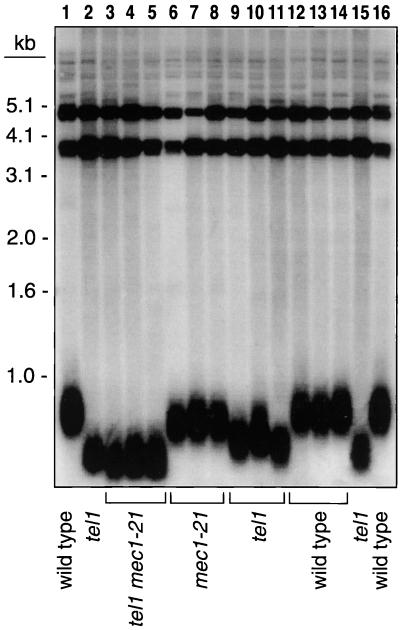
FIG. 1.
Telomere lengths in wild-type, tel1, mec1-21, and tel1 mec1-21 strains. A diploid strain heterozygous for tel1 and mec1-21 mutations was sporulated, and tetrads were dissected. In three tetrads in which all four genotypes were represented, DNA was isolated from spore cultures without subculturing; the strains had undergone about 35 cell divisions at the time of DNA extraction. The DNA was treated with PstI, and Southern analysis was performed. Strains analyzed: W303a (lanes 1 and 16); KRY20a (lanes 2 and 15); JMY300-1a, -2a, -3a (lanes 3 to 5, respectively); JMY300-1c, -2d, and -3d (lanes 6 to 8, respectively); JMY300-1d, -2b, and -3b (lanes 9 to 11, respectively); JMY300-1b, -2c, and -3c (lanes 12 to 14, respectively). Since the tel1 mutation exhibits a long phenotypic lag (20), the telomeres in the tel1 control strain KRY20a (lane 2), which had been subcultured for more than 100 doublings, were slightly shorter than those in the tel1 strains derived from the spores, which had not been subcultured.