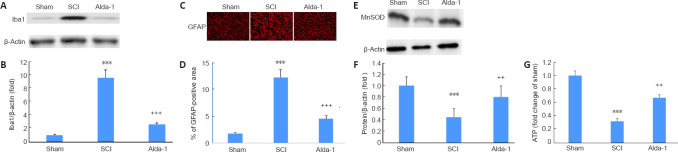
Figure 8.
ALDH2 agonist Alda-1 treatment of SCI decreases the activation of Iba-1 and GFAP and normalized mitochondrial oxidative stress measured as the expression of MnSOD in the chronic phase (30 days) of a mouse model of SCI.
Western blot of Iba-1 showing microglial activation (A) and densitometry (B). Immunohistochemistry of GFAP showing the expression of reactive astrocytes (C; red) and densitometry (D). Western blot of MnSOD and its densitometry (F) showing the change in mitochondrial redox. ATP content was measured by a luciferase-based assay showing that Alda-1 improved the ATP level (G). Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 7). ***P < 0.001, vs. Sham; ++P < 0.01, +++P < 0.001, vs. SCI (one-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s post hoc test). Alda-1: N-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)-2,6-dichlorobenzamide; ALDH2: aldehyde dehydrogenase 2; GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein; Iba-1: ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1; SCI: spinal cord injury.