Figure 1.
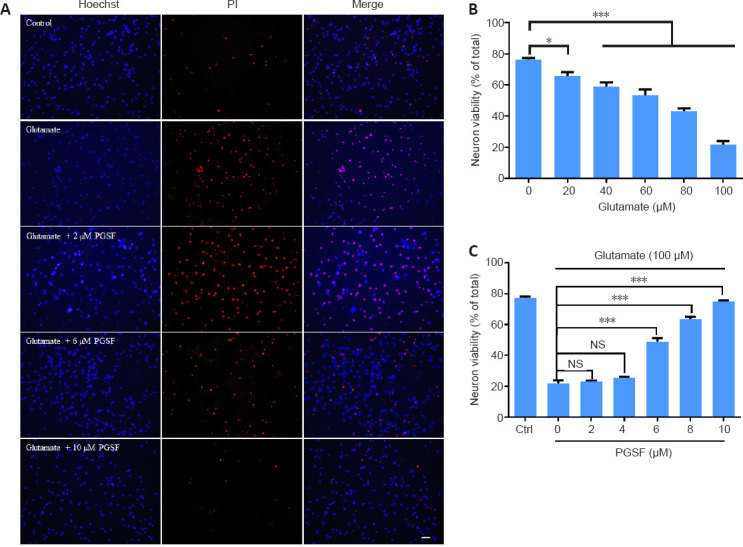
PGSF inhibits glutamate-induced death of cultured hippocampal neurons.
Cells were treated for 24 hours with glutamate alone or in the presence of PGSF (2, 6, 8, or 10 µM), and neuronal death was detected by Hoechst 33342 (blue) and PI (red) staining. (A) Representative images of neurons under control conditions and after treatment with glutamate (100 µM) alone or in the presence of PGSF. Cells stained with Hoechst 33342 only are surviving cells, and those co-stained with Hoechst 33342 and PI are dead cells. Scale bar: 20 μM. (B) Quantitative analysis of neuronal viability after treatment with different concentrations of glutamate. The experiment was repeated four times. (C) Quantitative analysis of neuronal viability in cultured cells treated with 100 µM glutamate in the presence of different doses of PGSF. The experiment was repeated nine times. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 (one-way analysis of variance followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test). Original data for Figure 1 are shown in Additional file 2. NS: Not significant; PGSF: polygalasaponin F; PI: propidium iodide.
