Figure 1. Obesity Is the Major Cause of Insulin Resistance in Humans and Is a Driver of the Global Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Epidemic.
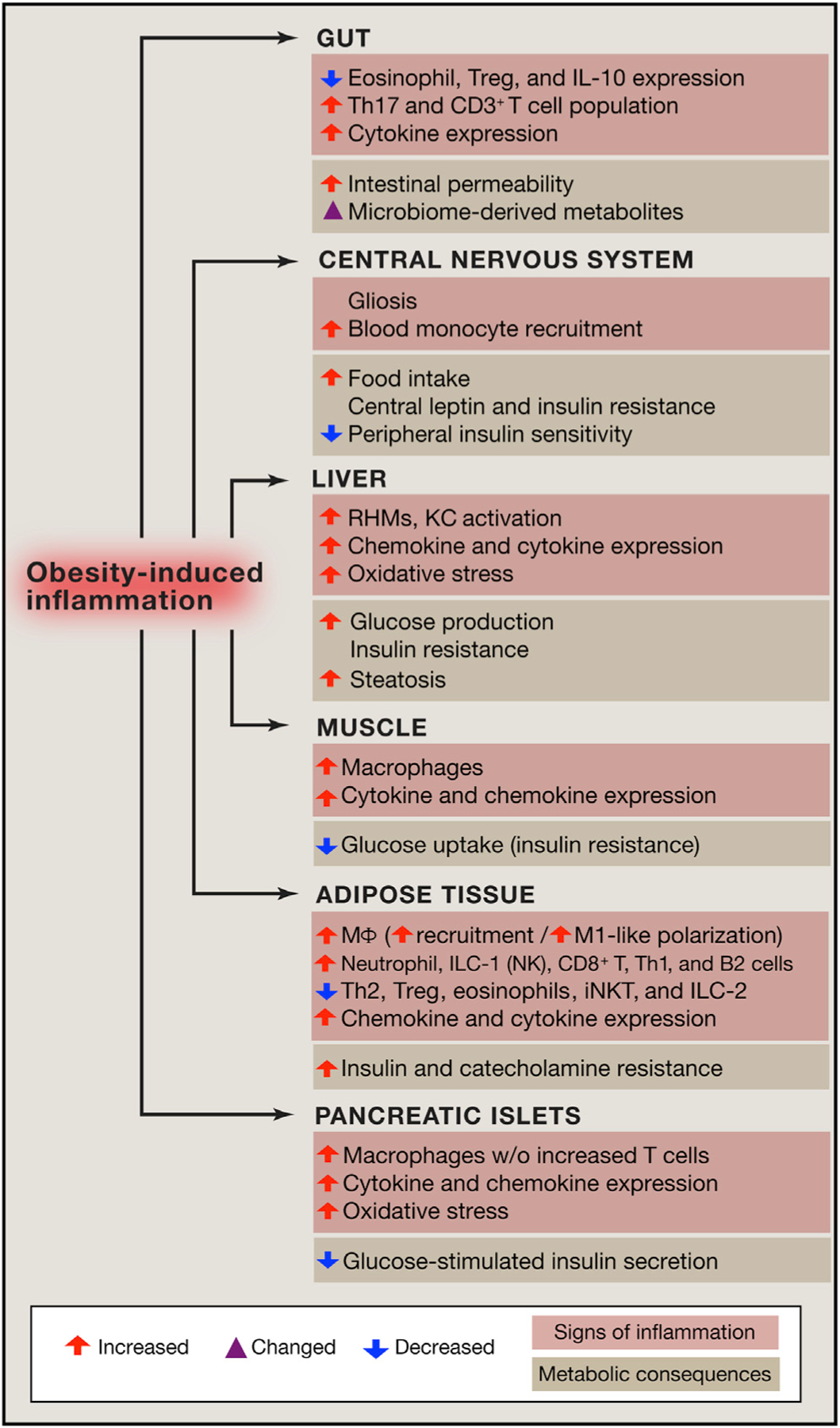
Obesity-induced chronic tissue inflammation is a key mechanism of the dys-metabolism that occurs in this condition. Chronic tissue inflammation induces a range of effects on adipose tissue, muscle, liver, pancreatic islets, the gut, and the CNS. These inflammatory changes contribute to insulin resistance (adipocytes, muscle, liver), decreased insulin secretion (islets), dysbiosis and intestinal permeability (gut), and increased food intake (CNS).
