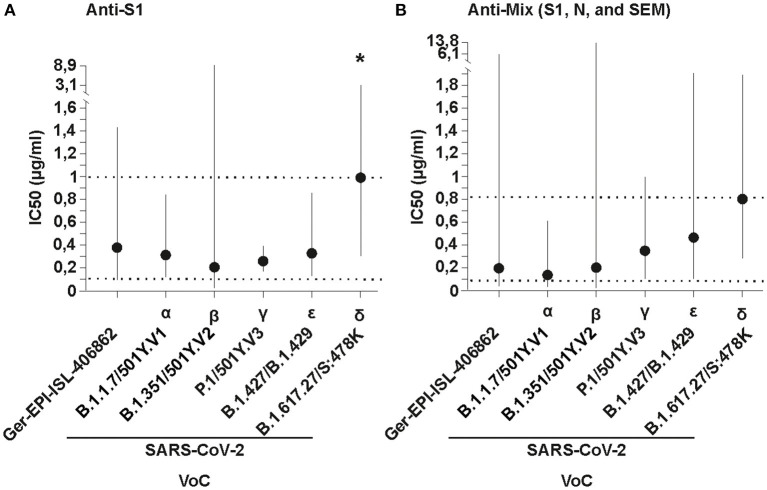
Figure 1.
In vitro neutralizing potency of (A) Anti-S1 (S1 SARS-CoV-2 recombinant protein) and (B) Anti-Mix (mixture of S1, N, and SEM mosaic SARS-CoV-2 recombinant proteins of Wuhan-Hu-1, Accession N YP_009724390.1) polyclonal antibodies purified from the plasma of hyperimmunized horses against different SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VoC) and an early isolate, named using WHO and Pango/Nextrain designations (strains used = GERMANY/GISAID EPI_ISL 406862, BetaCoV/ChVir21652, hCoV-19/Aruba_11401/2021, hCoV-19/Netherlands/NoordHolland_10915/2021, BetaCoV/ChVir22131/B.1.351/501Y.V2, SARS-CoV-2/CSpecVir25702_4/B.1.617.2 p.1, VS 09.07.2021 acquired from https://www.european-virus-archive.com/evag-news/sars-cov-2-collection). The inhibitory concentration (IC50) in plaque reduction neutralization tests (PRNT) was calculated using a non-linear regression analysis in the GraphPadPrism 5 software. Potencies (IC50) were not statistically different among viral variants with the Anti-Mix formulation, and the null hypothesis was not rejected, meaning the IC50 was equal in all datasets. The potencies (IC50) for the Anti-S1 formulations were significantly different, meaning the IC50 differed between formulations, but only when the delta VoC was added (denoted by an asterisk). Dotted lines denote the mean minimum and maximum concentrations and vertical solid lines denote 95% confidence intervals for both formulations.