Fig 4. HNRNPL is required for Pol II–mediated transcription of integrin/ECM genes.
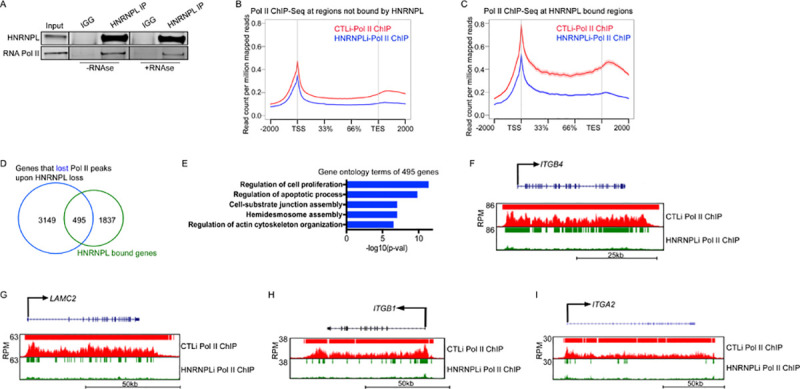
(A) IPs were performed using an HNRNPL antibody or IGG and western blotted for HNRNPL or RNA Pol II protein expression. IPs were performed +/− RNase A. A total of 1% of the cell lysate was used as input. Representative blots are shown. (B) RNA Pol II ChIP-Seq at regions not bound by HNRNPL in CTLi (red) and HNRNPLi (blue) cells. Y-axis is shown as read count per million reads, and X-axis is the distance along genes. TSS is transcription start site, and TES is transcription end site. Pol II ChIP-Seq in CTLi and HNRNPLi cells were performed in duplicates. (C) Pol II ChIP-Seq at regions bound by HNRNPL in CTLi (red) and HNRNPLi (blue) cells. (D) Overlap between HNRNPL bound genes (HNRNPL ChIP-Seq) and genes that lost Pol II peaks upon HNRNPL knockdown. (E) GO terms of the 495 genes that overlap from (D). (F–I) Gene tracks of ITGB4 (F), LAMC2 (G), ITGB1 (H), and ITGA2 (I). Pol II ChIP-Seq is shown in CTLi (red) and HNRNPLi (green) cells. Y-axis shows RPM, and red or green bar over gene tracks represents significant peaks. X-axis shows position along gene. Primary data for this figure can be found in S1 Data. ChIP-Seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing; ECM, extracellular matrix; GO, gene ontology; HNRNPL, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L; IGG, immunoglobulin; IP, immunoprecipitation; Pol II, polymerase II; RPM, reads per million.
