Figure 1. Increased affinity of APN01 interactions with SARS-CoV-2-RBD variants.
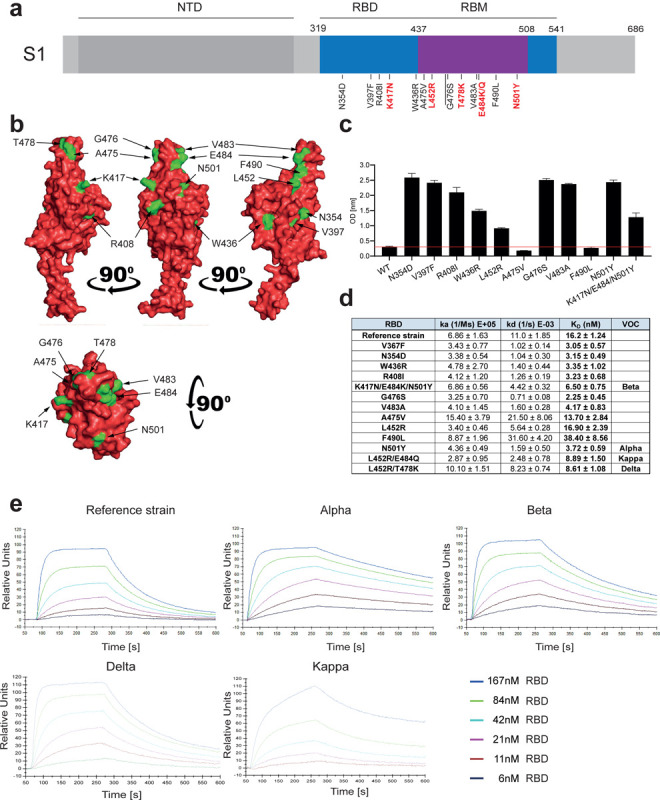
(a) Schematic depicts structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein S1 domain. Indicated is the amino terminal domain (NTD), the receptor binding domain (RBD) in blue and within the RBD the receptor binding motif (RBM) in purple. Numbers above depict domain boundaries. Mutations within the RBD/RBM are indicated below with observed amino acid exchanges. Shown in red are mutations observed in Variants of Concern (VOC). (b) PyMOL rendered visualization of the SARS-CoV-2 RBD. Rendering depicts the SARS-CoV-2 RBD with mutation sites shown in green. (c) ELISA analysis showing the binding strength of SARS-CoV-2 RBD carrying the indicated mutations to APN01. Axis labels indicate the SARS-CoV-2 RBD variant substitutions tested. (d) Surface Plasmon Resonance analysis to derive kinetic constants (ka, kd) and affinity values (KD) of SARS-CoV-2 RBD/APN01 interaction. The table lists both the tested variants and the introduced amino acid substitution as well as the designation of the respective Variants of Concern mutations tested in this study. Reference strain RBD sequence corresponds to the Wuhan SARS-CoV-2 isolate (e) Representative SPR sensorgram images for the SARS-CoV-2 RBD/APN01 interaction.
