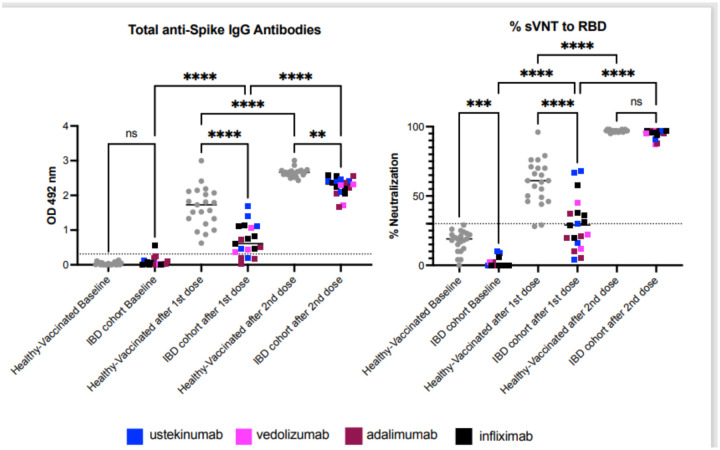
Figure 1: Patients with IBD on biologics show a limited humoral immune response to COVID-19 vaccine.
The figure shows the results for 19 subjects with IBD compared with 21 healthy volunteers. Samples correspond to baseline (before vaccination), and 2-weeks after the first and the second Pfizer Covid-19 vaccine doses. In average samples were collected 14 days after each dose. Samples from 21 healthy volunteers were available for comparison and were collected prior to vaccination (baseline) and in average 15 to 20 days after each dose. Of the 21 healthy volunteers, eighteen (18) received Pfizer’s vaccine and three (3) Moderna’s formulation. Panel A shows the total anti-Spike S1 IgG antibodies. Results show that one vaccine dose in IBD patients triggers a limited antibodies response which is significantly lower compared to the healthy cohort. Five patients with IBD had no detectable antibodies after the first dose. After the second dose all IBD patients had detectable antibodies, however they were still significantly lower compared to the healthy control group. Panel B shows the antibodies’ blocking capabilities measured by a surrogate viral neutralization assay (sVNT) and results are provided as percentage of neutralization. After the first vaccine dose, only 38% of IBD patients developed neutralizing activity (n=8) compared with 90.4% of the healthy individuals (n=19). Three (3) patients with IBD developed borderline neutralizing activity and 47.6% (n=10) did not develop neutralizing activity. The second vaccine shot boosted the neutralizing activity and 100% of the patients had detectable neutralizing activity with a magnitude similar to the healthy cohort. Interestingly, and as a potential consequence of the immunosuppression therapy, the blocking baseline activity of the healthy individuals is significantly higher than the IBD group. However, all those values were below the detection threshold. The threshold for the total antibodies was 0.312 and for the blocking activity was 30%. Statistical significance was determined by One-way ANOVA multiple comparisons to test for increase or decrease among samples. Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was performed as post-hoc test p<0.05 was considered significant.