Figure 2. Patients with more severe COVID-19 have higher antibody levels against SARS-CoV-2.
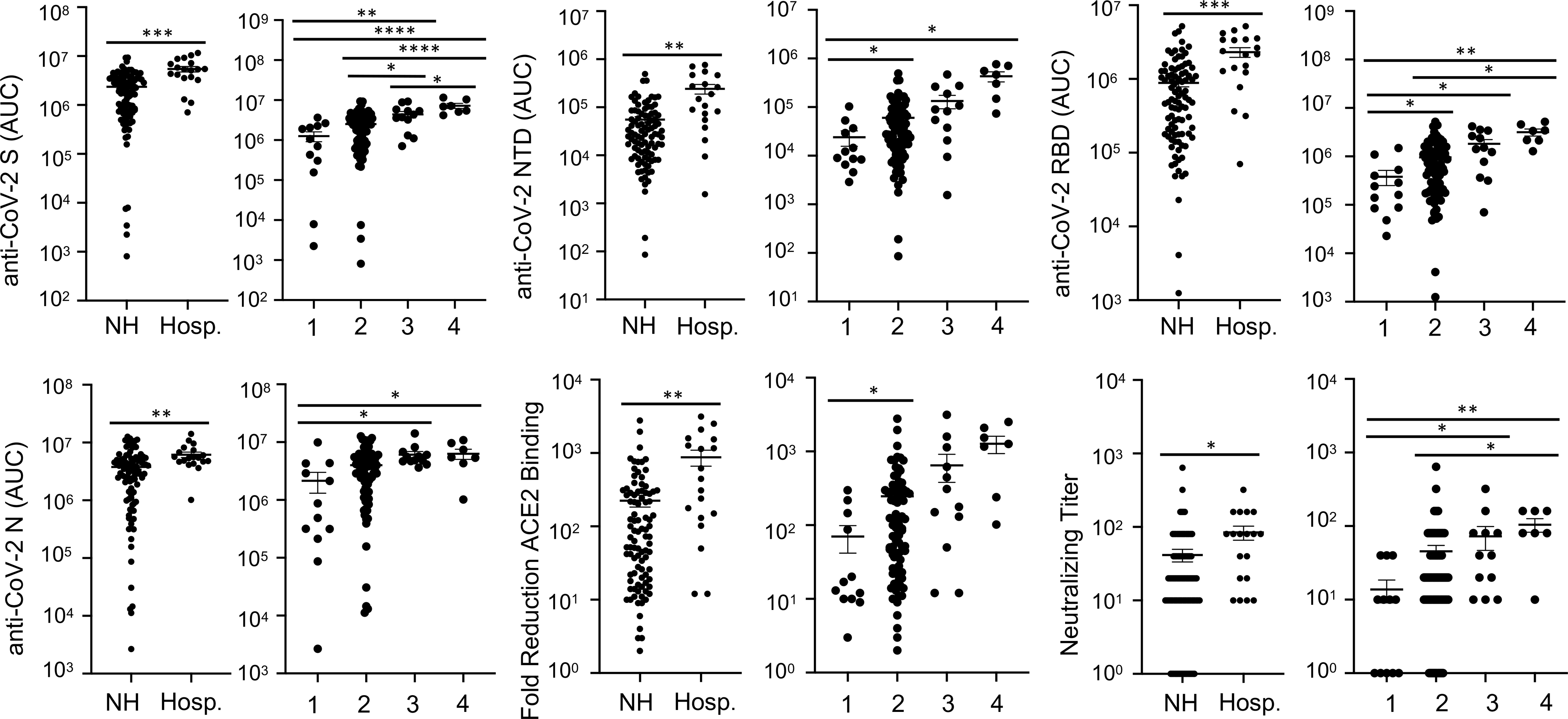
IgG levels against SARS-CoV-2 S, NTD, RBD, and N, as well as fold reduction of RBD-ACE2 binding, and neutralizing antibodies in COVID-19 convalescent sera five weeks post-symptom resolution were compared for non-hospitalized (NH, n=94) versus hospitalized (Hosp., n=19) subjects by t test and among subjects with mild (score 1, n=12), moderate (2, n=82), severe (3, n=12), and critical (4, n=7) COVID-19 severity by ANOVA (anti-NTD, anti-RBD, and RBD-ACE2 binding inhibition by Welch’s ANOVA with Dunnett’s test; anti-S and anti-N by ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, and neutralizing titers by Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test). For all panels: lines indicate mean +/− SEM; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
