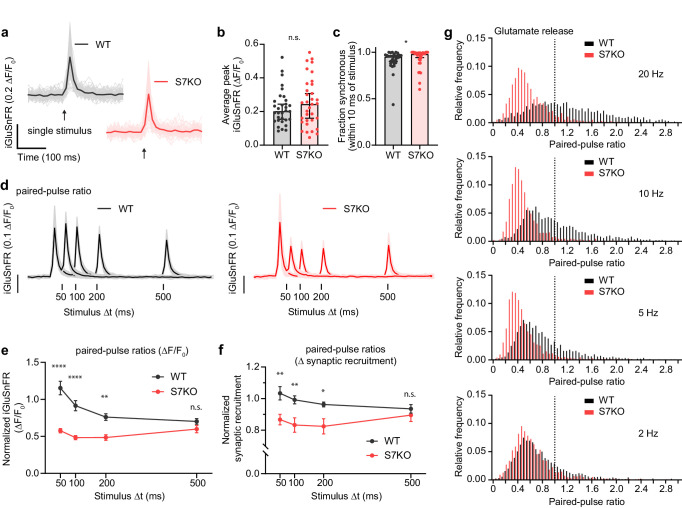
Figure 1. SYT7 influences presynaptic neurotransmitter release during short-term synaptic plasticity.
(a) Representative super-folder iGluSnFR S72A (hereon iGluSnFR) traces from single-stimulus experiments. Lighter traces are individual regions of interest (ROIs) and dark bold traces are the average of all light traces from a full field of view (FOV); the single stimulus is denoted with an arrow. Wild-type (WT) are denoted in black and gray, and SYT7KO are represented in red and light red; same scheme applies throughout the figure. (b) Peak iGluSnFR signals between WT (0.203 [95% CI 0.154–0.244] ΔF/F0) and SYT7KO (0.245 [95% CI 0.160–0.308] ΔF/F0). Values are medians with 95% CI representing error, Mann-Whitney test, p = 0.4554, each n is a separate FOV (n = 32 (WT) and 34 (SYT7KO) from four independent experiments). (c) Fraction of synchronous release, defined as peak iGluSnFR signals arriving within 10 ms of stimulus from total release of 500 ms following the stimulus, compared between WT (0.9522 [95 % CI 0.902–0.965]) and SYT7KO (0.9808 [95% CI 0.943–0.993]). Data from the same n as in (b). Values are medians with 95% CI representing error, Mann-Whitney test, *p = 0.0326. (d) Average +/- standard deviation traces from paired-pulse ratio (PPR) experiments with four interstimulus intervals compared; n = 14 (WT 20 Hz), 14 (WT 10 Hz), 15 (WT 5 Hz), 13 (WT 2 Hz), 15 (SYT7KO 20 Hz), 13 (SYT7KO 10 Hz), 14 (SYT7KO 5 Hz), 13 (SYT7KO 2 Hz) from three independent experiments. (e) Quantification of PPR (peak iGluSnFR ΔF/F0) from WT and SYT7KO; values are means +/- SEM. ****p<0.0001, **p = 0.0012, by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test; full statistics are provided in Figure 1—source data 1. (f) Quantification of fractional active synapses, that is, the number of synapses demonstrating peak release above baseline during the second stimulus relative to the first of a paired pulse. Values are means +/- SEM. **p = 0.0052, **p = 0.0099, and *p = 0.0289, in order from left to right, by two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test; full statistics are provided in Figure 1—source data 2. (g) Relative frequency histograms of PPR from all ROIs quantified from PPR trials, 20 Hz, 10 Hz, 5 Hz, 2 Hz, WT, and SYT7KO. Vertical dotted line delineates a PPR of 1.