Figure 3.
MEAs pose a reliable platform for genotype-phenotype correlations
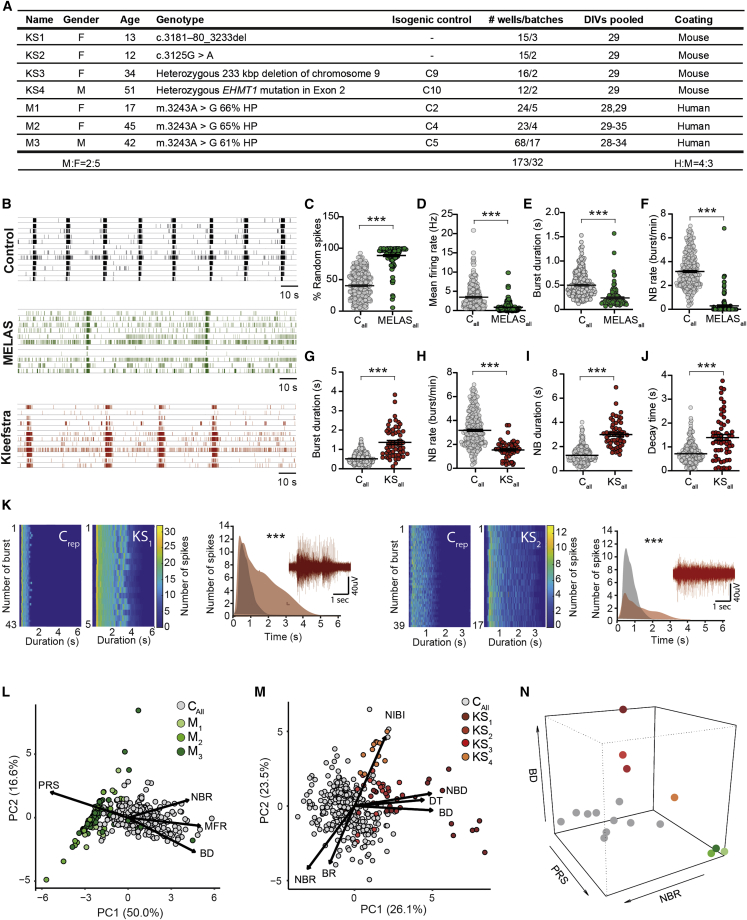
(A) Information regarding the seven patient lines included in this study. Isogenic controls represent the lines made from the same founder somatic cell line. Number of wells represents total number of wells recorded for that line between DIV 27 and 35, including the number of batches. Some batches overlap between lines.
(B) Representative raster plots showing 3 min of electrophysiological activity from control, MELAS, and KS patient lines.
(C–F) Graphs showing the values of four MEA parameters, including (C) PRS, (D) MFR, (E) BD, and (F) NBR for control and MELAS neuronal networks (mean ± standard error of the mean).
(G–J) Graphs showing four MEAs, including (G) BD, (H) NBR, (I) NBD, and (J) DT for control and KS neuronal networks (mean ± standard error of the mean). Mann-Whitney U test with Bonferroni correction for multiple testing was used to compare between patient lines and their isogenic controls (Table S4).
(K) Representative network burst alignment from one recording of a representative control and KS1, and a representative control and KS2. Inset: extracted burst shape and representative raw trace of a network burst (sample size for C representative: C6, n = 58, C9, n = 12, KS1, n = 15, KS2, n = 15, multiple t test on bins using the Holm-Sidak method, p < 0.0001 for both comparisons).
(L) PCA plot on 7 MEA parameters, showing parameters that explain the differences in network behavior between Call (278 wells from 10 control lines) and M1-3.
(M) PCA plot on 12 MEA parameters, showing parameters that explain the differences in network behavior between Call and KS1-4.
(N) 3D scatterplot showing PRS, BD, and NBR for all MELAS (green), KS (red), and control lines (gray).
∗∗p = 0.01 and ∗∗∗p = 0.001. DIV, days in vitro; MFR, mean firing rate; PRS, percentage of random spikes; BD, mean burst duration; NBR, network burst rate; NBD, network burst duration; DT, decay time. All means, p values, and statistic tests used are reported in Table S4.