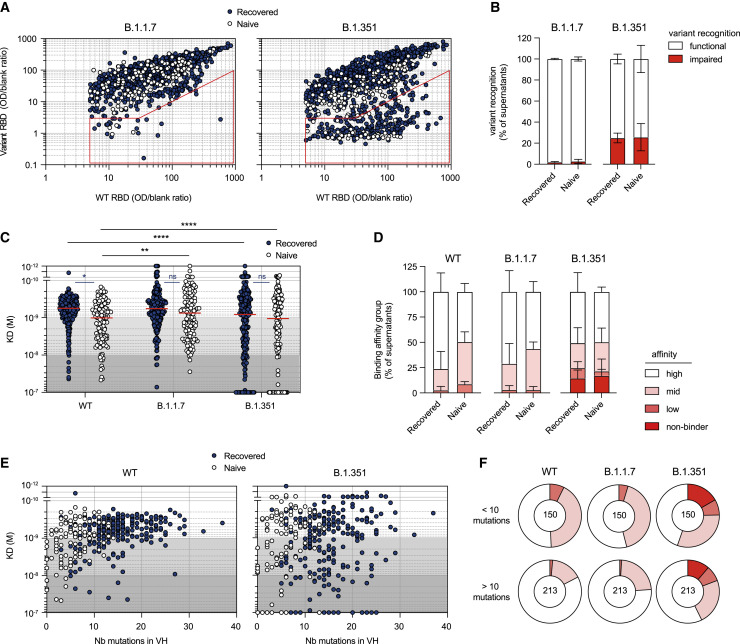
Figure 4.
The MBC pool of vaccinated individuals contains high-affinity clones against WT SARS-CoV-2 and B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 VOCs
(A) WT RBD versus B.1.1.7 RBD (left) or B.1.351 RBD ELISA values (right) for all single-cell culture supernatants of RBD-specific MBCs isolated from SARS-CoV-2-recovered (dark blue, n = 952) and naive (white, n = 373) donors. Only supernatants with WT ELISA OD/blank ratio ≥ 5 are displayed. The red sector identifies naturally expressed antibodies defined as impaired in the recognition of a given variant (variant ELISA OD/blank ratio < 3 or ≥ 10-fold decrease in variant recognition).
(B) Frequencies of single RBD-specific MBC culture supernatants with functional or impaired recognition of B.1.1.7 or B.1.351 RBD variants as assessed by ELISA.
(C) Dissociation constants (KD, expressed as moles/L) measured by BLI for 382 naturally expressed monoclonal antibodies against WT, B.1.1.7, and B.1.351 RBD. Tested monoclonal antibodies were selected randomly from single-cell culture supernatants of RBD-specific MBCs isolated from SARS-CoV-2-recovered (n = 251) and naive donors (n = 131) and displaying WT RBD ELISA OD/blank ratio ≥ 3. Background colors define high-affinity (KD < 10−9 M), mid-affinity (10−9 ≤ KD < 10−8 M), and low-affinity (10−8 ≤ KD < 10−7) monoclonal antibodies. All monoclonal antibodies with no measurable affinity (KD ≥ 10−7) were considered non-binders.
(D) Histogram showing the intra-donor binding affinity distribution of monoclonal antibodies tested against WT, B.1.1.7, and B.1.351 RBD variants, as defined in (C), for SARS-CoV-2-recovered or naive donors. Bars indicate mean ± SEM.
(E) Measured KD (M) against WT (left) or B.1.351 RBD (right) versus number of VH mutations for all tested monoclonal antibodies with available VH sequence from SARS-CoV-2-recovered (dark blue, n = 249) and naive (white, n = 114)) donors (Spearman correlations for all sequences: VH mutation/WT KD, r = 0.3791, p < 0.0001; VH mutation/B.1.351 KD, r = 0.152, p = 0.0033).
(F) Pie chart showing the binding affinity distribution of all tested monoclonal antibodies with low (<10 mutations, top panel) or high VH mutation numbers (>10, bottom panel) against WT, B.1.1.7, and B.1.351 RBD variants as defined in (C). Numbers at center of the pie chart indicate the total number of tested monoclonal antibodies in each group.
A two-way ANOVA with two sets of multiple comparisons (between tested variants inside each group (black lines) and between groups for each tested variants (colored lines)) was performed (C; Benjamini, Krieger and Yekutieli FDR correction). ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗p < 0.05. See also Figure S4 and Table S2.