Figure 3.
Chd4 maintains the transcriptional identity of SCs during muscle regeneration
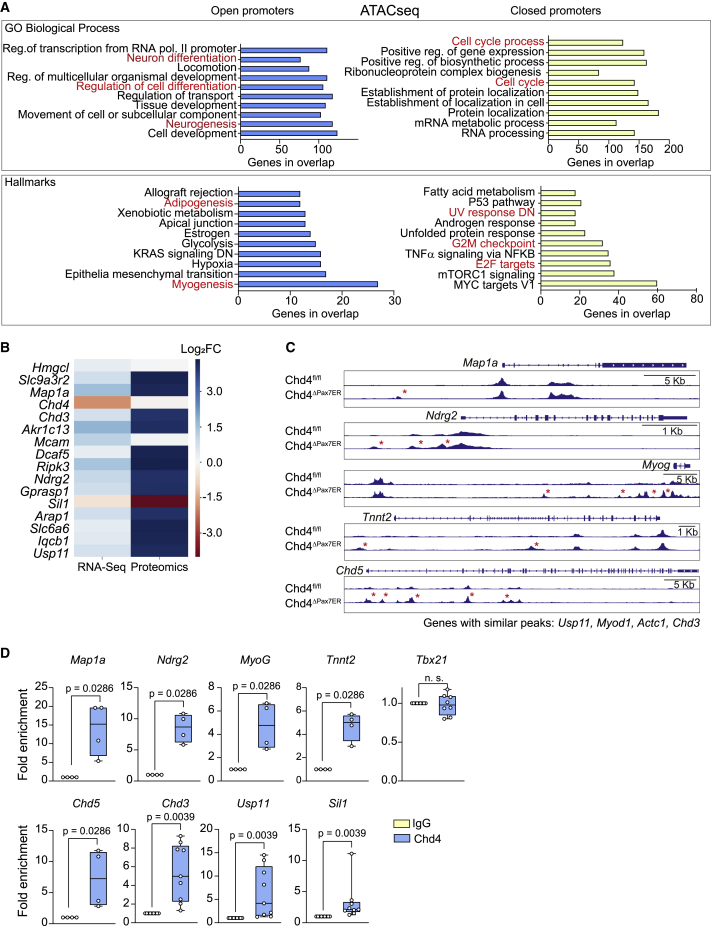
(A) GO analysis of the genes with differential open (left) and closed (right) chromatin from SCs obtained from TMX-treated Chd4fl/fl or Chd4ΔPax7ER mice at 3 days after muscle injury (n = 4 mice/group). Data were analyzed using gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) (MySigDB 6.2 Database). Reg, regulation; pol, polymerase. All categories represented obtained p < 0.0001.
(B) Color map (coded for Log2(fold change)) representing targets commonly found to be differentially expressed (p < 0.01) in the RNA-seq and protein mass spectrometry of Chd4fl/fl SCs transduced with Ad-CRE or Ad-GFP (n = 4 independent experiments). Data were analyzed using DESeq2 (RNA-seq) or MaxQuant (mass spectrometry).
(C) Genome browser tracks of ATAC-seq data at the Map1a, Ndrg2, Myog, Tnnt2, and Chd5 loci from SCs obtained from TMX-treated Chd4fl/fl and Chd4ΔPax7ER mice at 3 days after muscle injury (overlayed tracks of n = 4 mice).
(D) ChIP-qPCR of Chd4 protein binding to the indicated gene loci. The Tbx21 gene was used as control. Data were normalized to immunoglobulin G (IgG), which was set to 1 (n = 4 independent experiments).