Figure 7.
HNF1B haploinsufficiency impairs the early stage pancreatic developmental program by altering expression of key non-canonical Wnt and Hippo signaling pathway components
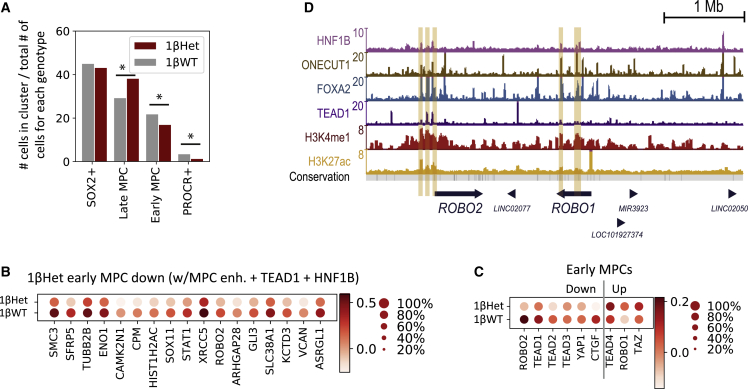
(A) The distribution of clustered cell types by genotype. The numbers of clustered 1βWT and 1βHet cells were normalized independently by genotype; the sum of all red bars accounts for 100% of 1βHet cells and that of the gray bars for 100% of 1βWT cells.∗p < 0.001.
(B) Dot plot showing the expression of genes significantly downregulated in 1βWT and 1βHet early MPCs. Genes were filtered by the association with at least one MPC enhancer (as previously defined in Cebola et al., 2015) that presents both TEAD1 and HNF1B ChIP-seq enrichment. Color intensity indicates mean expression (normalized) in a cluster, dot size indicates the proportion of cells in a cluster expressing the gene.
(C) Dot plot showing expression of ROBO1, ROBO2, selected Hippo pathway components, and its known target CTGF in 1βWT and 1βHet early MPCs. Color intensity indicates mean expression (normalized) in a cluster, dot size indicates the proportion of cells in a cluster expressing the gene.
(D) UCSC genome browser snapshot of the ROBO1 and ROBO2 genomic locus. ChIP-seq was used to locate binding sites of HNF1B, ONECUT1, FOXA2, and TEAD1 in MPCs (data from Cebola et al., 2015). ChIP-seq for H3K4me1 and H3K27ac histone modifications denotes the epigenomic printing of active enhancers. MPC enhancers enriched in HNF1B signal in this locus are highlighted in light orange.